Updated: 28/06/2023
Stories abound of startup companies all around the globe, making it big and, in turn, making their investors extremely wealthy, this often makes one wonder how to invest in startups? Investing in a company at the very beginning of its lifecycle can prove to be very profitable. Often with great risk, comes great reward.
If you had invested just $10,000 in Amazon, Dell, Apple, or Microsoft, when they went IPO, you’d be a million dollars richer just from that investment according to the IPO Playbook.
What is a Startup?
Let us quickly run over the basics on how to invest in startups, starting with understanding the definition of a ‘startup’. A startup refers to a company in the first stages of operations. Startups are founded by one or more entrepreneurs who want to develop a product or service for which they believe there is demand. These companies generally start with high costs and limited revenue, which is why they look for capital from a variety of sources.

Understanding the components, nature and the business model of a startup before you decide to invest your money and time is important. There are a few special considerations that you need to consider when it comes to startups, this will make you decide when and how to invest in startups.
Location
Startups must decide whether their business is conducted online, in an office or home office, or in a store. The location depends on the product or service being offered. For example, a technology startup selling virtual reality hardware may need a physical storefront to give customers a face-to-face demonstration of the product’s complex features.
In your decision to how to invest in startups, this is important for you to know where the startup plans to operate and what exactly will you be investing your money and time into. Whether it will be based offline or on an online-based platform.
Funding
There are many ways that startups are funded according to research by Santa Clarita Valley. In order to understand how to invest in startups, you first need to identify yourself and your source of funding to the startup amongst the following.
Read more on Startup Capital here!
How Are Startups Funded?
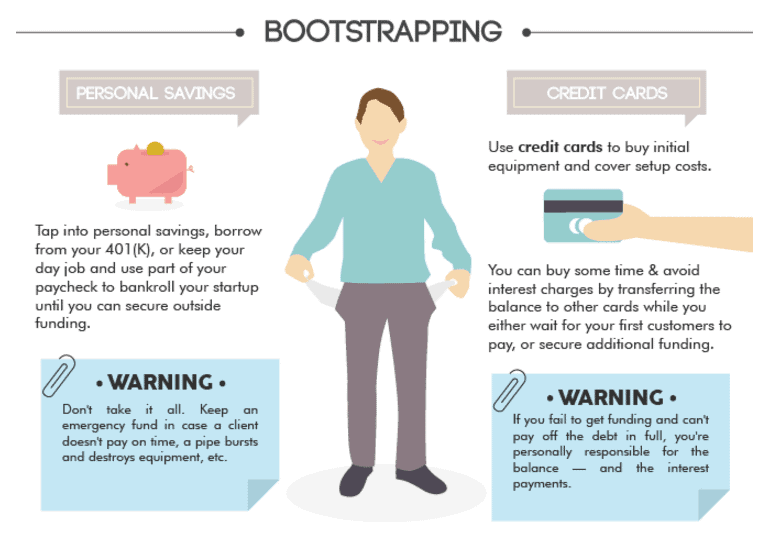
- Bootstrapping (self-financing): This refers to funding the startup using personal savings, assets, or revenue generated from the business itself. Bootstrapping allows founders to maintain full ownership and control over their venture. However, it may not always be feasible due to the substantial costs involved, and there is a risk of losing personal funds if the business fails.
- Taking out a loan: Another option is to secure financing by obtaining a loan from a bank or financial institution. This approach enables founders to retain complete ownership of the startup. However, loan repayment, often with interest, begins immediately, and the loan application process can be complex and time-consuming.
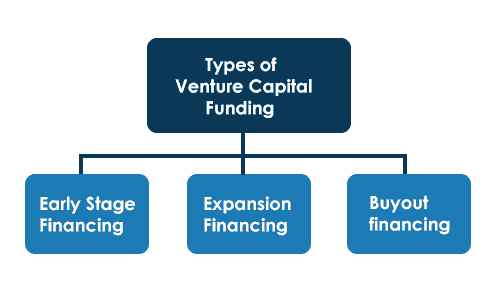
- Finding investors: Many startups raise capital by attracting investors who are willing to provide funding in exchange for equity or ownership stake in the company. Venture capital firms, angel investors, and crowdfunding platforms are common sources of investor funding. This approach is particularly popular for startups with high growth potential. Investors provide financial resources, expertise, and networking opportunities to support the startup's development. However, founders may need to give up a portion of their ownership and decision-making authority in return.
How To Invest In Startups
How do you find startups to invest in? There are so many ways online to be able to find startups in your own country to invest in based on the number of finances that you have. The platforms listed below offer a sampling of the avenues available to anyone who wants to invest in a startup with limited funds. While it’s unlikely that you’ll become the next Silicon Valley billionaire, these platforms can help diversify your broader investment portfolio and give you the satisfaction of supporting a young company you believe in. How to find startup companies to invest it? The listed below platforms will be your aid into finding startups.
-
WeFunder. Wefunder has a stated goal of funding more than 20,000 startups by the year 2029. It hopes to do this by accepting investments of as little as $100 at a time. Through Wefunder, an average investor can inject capital into a wide range of companies. At last glance, it was accepting investments into dozens of companies including a fan-owned entertainment company, a vegan marketplace, a dog cancer cure, and a brewing company, answering the question of how to invest in startups and where to find them.
-
Seed Invest. SeedInvest is a crowdfunding platform that allows individuals insight on how to invest in startups, to invest in early-stage companies that have been pre-screened for potential viability. According to SeedInvest, less than 1% of companies that seek funding through the platform are accepted. The company claims it has more than 250,000 investors, with more than 150 companies successfully funded.
When you sign up for an account on SeedInvest, you are presented with a list of companies seeking money. Many companies are open to receiving investments from anyone, but some require large investments and are open only to accredited investors who had an income exceeding $200,000 in each of the past two years. You are provided with a “pre-money valuation” as well as the total value of funds being sought and the amount already raised. Each company has its own minimum investment requirement and a time by which the money needs to be raised.
From the perspective of companies and how to invest in startups, NEXEA Group Sdn Bhd (Formerly known as NEXEA Angels Sdn Bhd) offers startup support as well as investing in startups.
- NEXEA Angel Investors. NEXEA Investors/Mentors seek investment opportunities in technology startups which can showcase revenue and potential future growth. NEXEA’s Angel Investors are all experienced business owners and/or C-level professionals who are able to provide more than just funding for your startup. We also provide mentorship & support through industry experts & mentors.
The video below answers this question in more details adding to more questions in terms of how to invest in startups specifically.
Startup Investing Process
The startup investing process is part of our initial question to “How to Invest in Startups?”. There are a few important steps that need to be done before the investing process begins.
- Preliminary steps: preliminary steps include a business plan – a detailed case for your business, which will include your market research, any traction to date, financial forecasts, the amount of investment being sought, and for what. Pitch Deck – you will present and send this out as reading material, so prepare two versions tailored to your investors.
An executive Summary – this is the written ‘elevator pitch’ for your business. Investors should want to read more but not be left wondering what the core of the business is.
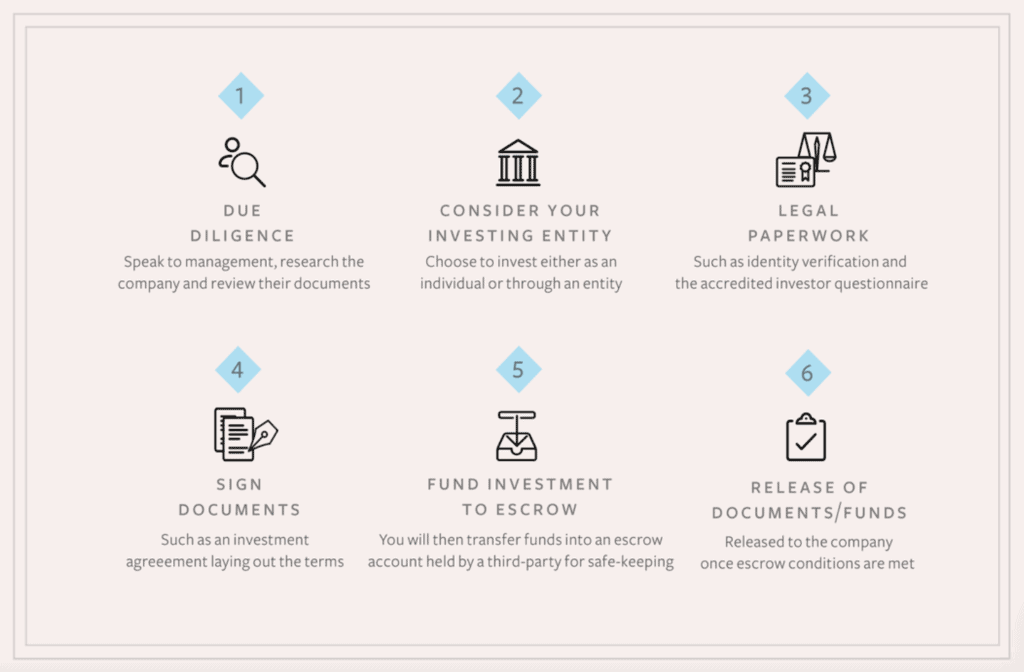
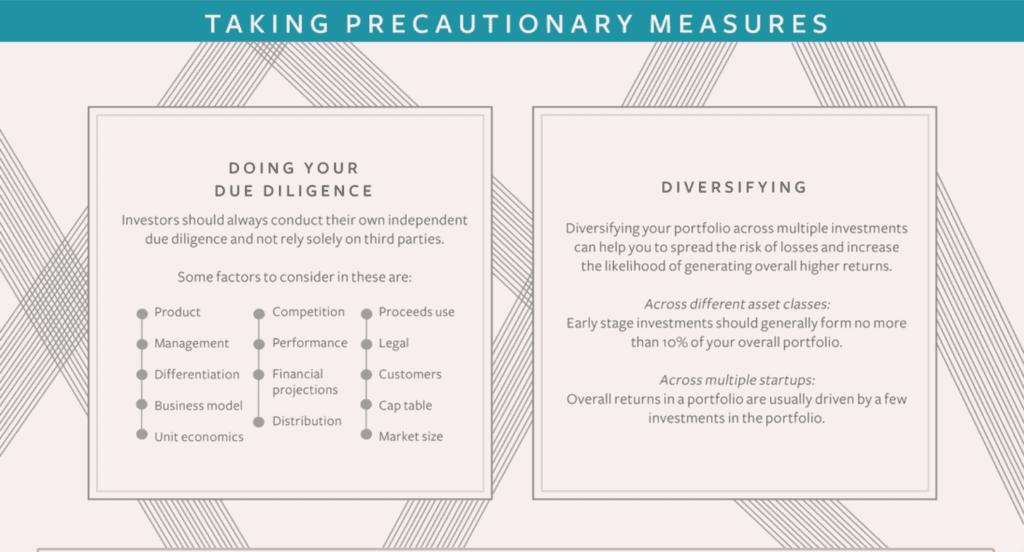
- Due Diligence: Due diligence is the term given to the investigatory work done around a transaction such as investment where the investor conducts detailed research into the financial, corporate and contractual status of your company. Your investors will usually make a preliminary request for you to provide documents which will include: corporate information, budgets, forecasts, key supplier/customer contracts in place, employee-employment contracts, schedule of intellectual property, a schedule of property or leases, a list of equipment owned by the company, details of other investors, shareholders, and bank loans, any existing or future litigation, tax and VAT filings and insurance documentation, and, if applicable, your data protection policies.
- Consider investing entity. Correct legal structure – it is worth noting that you can’t give away shares in your business in exchange for investment monies unless you have a legal entity with shares, i.e. a private limited company. So, if at the moment you are operating as a sole trader, or you haven’t started trading yet but intend to seek investment in the future, you will need to incorporate as a company and transfer all property owned by the ‘business’ into the company name.
- Legal paperwork. Once terms have been agreed and the due diligence has been completed, your (or the investor’s) solicitor will start to prepare the long-form documentation which will implement the funding arrangement. The following documentation will usually be involved: Shareholder’s Agreement or Investment Agreement, Vesting Provisions, Subscription Agreement, Articles of Association etc.
Sign and release of documentation.
Once you have external investors, your accounts and bookkeeping will need to be in immaculate condition and completely up to date. You will probably also have reporting obligations as part of your investment terms so at any given time you may need to report on the financial health of the company.
The process of how to invest in startups does not just start and end with funding only, there is a lot of ‘behind the scenes’ work and effort that goes into finding and investing in the methods of how to invest in startups.
Startup Investments in Malaysia
How to invest in startups in Malaysia? This section will be solving this problem for you if you are an investor or anyone looking for startups to invest in Malaysia.
Joining NEXEA’s Angel Investor Club Malaysia as an angel investor gives you access to at least 1000+ companies per year to bring you about 3-10 quality investments each year. The companies are filtered via our proprietary Startup Fundamentals Methodology. Each startup has to pass our due diligence process, background checks, and investment committee.
NEXEA’s Angels not only teach you how to invest in startups but they also consist of experienced businessmen who own multi-national business, and who have exited via a trade sale, or IPO, or are currently running a listed company. This knowledge is particularly useful for new Investors, we encourage members to share their Investment & Business Experiences. Increase the success rate of startup investment together.
The NEXEA Angel Investors Network is available in Malaysia to sophisticated investors that can support young Entrepreneurs running startups only. This group includes those who are either considered as a High Net Worth Individual or a High-Income Earner.
Also, see our insight on how startups get funding in Malaysia in detail.
Risks and Rewards of Investing in Startups
Is investing in startups a good idea? The answer to how to invest in startups might seem like an easy process, but there are risks and rewards associated with it. According to Investopedia:
- Startup companies are in the idea phase and do not yet have a working product, customer base, or revenue stream.
- Around 90% of startup companies funded will not make it to the initial public offering (IPO).
- Investing in startup companies is a very risky business, but it can be very rewarding if the investments do pay off.
Several high-profile company success stories have proven that putting money into a startup is one of the few great ways to invest and reap high returns. Here’s what motivates investors to put their money into startups:
- Potential high profit. With good planning, startup investments can be very profitable. Pay attention to companies that provide solutions, bring value and develop new trends in the ever-evolving knowledge-based economy. All it takes is an original idea and a solid execution for a startup to become successful. There could be a huge return on your investment if you know the exact skill on how to invest in startups and understand how to grow them.
- Diversification. Startups are an asset class that allows you to explore a different investment channel. Investments are risky and a diverse portfolio means you can minimize the possibilities of taking a big hit during a downturn.
- Buy-out potential. Many startups are bought by large corporations that see them as a potential competitor or want to leverage the technology created by the startup. If the startup you invest in sells at a lucrative price, you’ll enjoy great returns on your investment.
Even with their growth potential, startups are considered high-risk investments since only a small percentage succeeds. Consider these cons before you dig further into how to invest in startups:
- High risk. As fruitful as it may be, you could invest in a company that never succeeds. Startup investments are high-risk and your return on investment depends on the new venture becoming a success. Some markets are extremely competitive or saturated and some business ideas simply don’t work. Take the time to carefully analyze the company you’re thinking about investing in to assess the chances of this startup.
- Personality and attitude of the owner. You are a highly experienced investor with extensive knowledge of how to invest in startups but many angels and VC investors indicate that the personality and drive of the company founders are just as, or even more important than the business idea itself. Founders must have the skill, knowledge, and passion to carry them through periods of growing pains and discouragement.
They also have to be open to advise and constructive feedback from inside and outside the firm. The success of a startup partially depends on how hard the entrepreneur behind the idea is willing to work. To alleviate this risk, get to know the entrepreneur better, find out the history of their past business ventures.
In Conclusion
To conclude, the process of how to invest in startups goes beyond just financing methods. If you feel that startups are a good investment option for you, make sure you, as an investor take the time to look for good business startups and allocate a small percentage of your portfolio to this type of high-risk investment.
Investing in startups is an excellent opportunity for investors to expand their portfolio and contribute to an entrepreneur’s success but investing in a startup is not foolproof. Even though a company may have strong cash flow projections, what looks good on paper may not translate to the real world. Taking the time to execute due diligence when researching a startup investment is something investors can’t afford to skip.
Investopedia
References
Investing in Startups Without Being Wealthy
Initial Public Offering (IPO) Playbook
More About Startups Investment
To lower the risk of market volatility, diversification is a popular investment strategy that involves purchasing various types of investments. It is a component of asset allocation, which refers to how much of a portfolio is invested in different asset classes.
The most popular asset classes are stocks, bonds, and cash (or cash equivalents). Investors will combine disparate assets (such as stocks and bonds) to achieve diversification so that their portfolio does not have an excessive amount of exposure to one particular asset class or market.
Numerous investment options are available to investors, each with unique benefits and drawbacks. To diversify your portfolio by asset class, within asset classes, and outside of asset classes, we've identified carefully 12 top tips :
12 Tips For a Diversified Portfolio
Discover The Importance Of Diversification
A diversified investment portfolio offers the best balance for your savings plan by assisting your overall investments in absorbing the shocks of any financial disruption. However, diversification goes beyond just the type of investment or classes of securities; it also includes the individual securities that comprise each class of security.
Invest across a range of sectors, interest rates, and time periods. For instance, even though the pharmaceuticals sector is one of the best-performing sectors during the Covid-19 pandemic, you shouldn't place all of your investments in it. Consider diversifying into other booming industries, like information or education technology.
Allocation Of Assets
Stocks and bonds are the two main categories of investment, generally speaking. Bonds are typically more stable with lower returns, whereas stocks are considered high-risk with low returns. Divide your funds between these two options to reduce your risk exposure. The trick is to find a balance between the two, or an equilibrium between risk and certainty.
Distribution of assets is frequently based on lifestyle and age. You can take a chance when you're younger by choosing stocks with high returns.
Subtracting your age from 100 and using the result as the percentage of stocks in your portfolio is a good allocation method. A 30-year-old, for instance, could maintain 70% in stocks and 30% in bonds.
However, a 60-year-old should limit their risk exposure; as a result, the stock-to-bond allocation should be 40:60. When making these choices, you might need to consider your family's finances.
You should be more careful with your investments if you contribute significantly to the family's expenses. It would reduce the amount of available capital, so you might want to play it safe by tilting more heavily towards bonds.
Evaluate The Qualitative Risks Of The Stock
Before buying or selling a stock, use qualitative risk analysis to reduce the unpredictability of the transaction. A qualitative risk analysis gives a project's success a grade based on a predetermined scale. You must evaluate the stock using particular criteria that show its stability or potential for success in order to apply the same principle.
These criteria will cover a strong business model, senior management's integrity, corporate governance, brand value, compliance with laws and regulations, efficient risk management procedures, dependability of the company's goods or services, and competitive advantage.
Invest Money For Cash In Money Market Securities
Certificates of deposit (CDs), commercial papers (CPs), and Treasury bills (T-bills) are examples of instruments used in the money markets. The simplicity of liquidation is these securities' main benefit. It's a risk-free investment because of the lower risk.
T-bills are the most risk-free marketable securities that can be purchased individually. These government securities, also known as g-secs, are issued by the Reserve Bank of India, the country's banking watchdog. They offer a perfect, safe alternative for making short-term investments.
G-secs are well known for their safety but not for their high returns. A G-sec is secure because it is protected from market fluctuations, but doing so also eliminates the possibility of making a significant profit, as with stocks. If you want to park your money in a secure location temporarily, you can invest in g-secs. Additionally, you can use it to balance out other "riskier" investments in your portfolio, like high-value, high-risk stocks.
Purchase Bonds With Regular Cash Flows
Mutual funds are regarded as a dependable and secure form of investing. However, many options exist for investing, earning interest, and redeeming within mutual funds.
Consider investing in mutual funds with systematic cash flow, also known as a systematic withdrawal plan (SWP), if you want access to your money while it is locked away in a savings plan. You can take a set amount out of these investments monthly or quarterly. You can personalise withdrawal by choosing a fixed amount or a percentage of profits.
A systematic transfer plan, also known as STP, is an alternative where you can transfer a set amount between various mutual funds. STP aids in keeping your portfolio in balance.
Providing access to investments at predetermined intervals is the goal in either scenario.
Adopt A Buy-Hold Approach
Your long-term savings plan is essentially your investment plan. You must therefore begin to think strategically and refrain from making snap decisions. Instead of using a continuous trading strategy, consider buy-hold. It entails maintaining a largely stable portfolio over time, despite market fluctuations.
It's a more passive strategy where you let your investments grow instead of constantly trading. Having said that, don't be afraid to reduce holdings that have grown too quickly or occupy more space in your investment portfolio than is necessary or wise.
Recognise Elements That Affect The Financial Markets
You must first comprehend the variables affecting the financial markets before investing. Stock exchanges, foreign exchanges, bond markets, money markets, and interbank markets are examples of financial markets. These essentially function as a market for financial instruments and, like any other market, are driven by supply and demand.
Like any other market, its dynamics are influenced by outside factors like interest rates and inflation. The other significant factor is the Reserve Bank of India, the country's central bank, and its monetary policies.
Gain Knowledge Of World Markets
The potential for quick, high returns exists in the global markets. These markets are typically characterised by a dynamic that moves extremely quickly and requires an investor to navigate numerous financial rules. It may take some time for a novice investor to become familiar with its workings, comprehend trends and fluctuations, and determine what causes these shifts. However, it can be very profitable, particularly when the Indian market is going through a protracted downturn.
Start with a mutual or exchange-traded fund (ETF) with a low-cost structure and lots of liquidity. It will enable you to invest safely with little capital, allowing you to observe and comprehend how the world market functions.
Regularly Rebalance Your Portfolio

Both in life and in investing, balance is crucial. It's critical to regularly review your investment portfolio to ensure that all of your assets are in balance. This assessment should be based on your objectives and significant life achievements and, where you started, and how far you have come.
Your investments should be compared to your lifestyle, and a financial advisor can also advise you on other possibilities. While keeping you informed of your investment's annual growth, this exercise also helps you become more disciplined. These two elements will eventually aid in your decision-making and help you better understand future investments.
Try A Disciplined Investment Plan
A SIP (systematic investment plan) is a good choice if you want to invest a small amount over time rather than a large sum simultaneously. With this approach, you can make fixed investments in mutual funds regularly. It is perfect for those who can only afford to invest a small amount each month but cannot access a large sum of money.
A SIP can be started with as little as 500 INR. Young investors should use SIPs because they help them develop discipline in their investment strategy. The investment amount is taken out of your bank account directly, which helps you get used to regularly setting aside a set amount of money for your future. Additionally, it makes your investment secure because it is based on compound interest and has a low overall risk.
Always keep in mind that diversification is the key. Invest in various industries and interest-format types.
Purchase Life Insurance
In India, few young adults consider purchasing life insurance. When you're young, it can be difficult to think about dying, especially if you don't have any children or other dependents. However, the conventional wisdom that life insurance should be treated as a crucial investment option is still valid, particularly when you are young, due to the low premium rates your insurance company will likely provide you with at a younger age.
The younger you are, the lower your premiums will be, according to how life insurance companies determine premiums. Even though you might not currently benefit from life insurance, your loved ones will be protected if you pass away.
By investing in unit-linked insurance plans (ULIPs), which combine life insurance with market-linked investments, you can also profit from your life insurance. The insurance premium is paid in part of the investment sum; the remaining sum is placed in the market. This is a long-term strategy, so getting started early can help you save for upcoming milestones. Always compare ULIPs before making an investment.
Recognise Your Financial Prejudices
You should be aware of the biases and beliefs likely to affect your investment decisions. Outside forces frequently influence us, particularly risk tolerance, familial character, good fortune, and cultural values.
Your level of risk tolerance is referred to as your risk aptitude, and it frequently depends on your family history and cultural norms. The likelihood of young adults from wealthy families choosing high-risk, high-return investments is higher. People from modest backgrounds, on the other hand, are more likely to invest in secure portfolios. Family values also impact how much we are willing to believe in luck.
The cultural influence on our investments is another distinctive quality. For instance, some communities favour gold investments, while others favour real estate.
About Investment Portfolio

Are Index Funds Diverse Enough?
An index fund or ETF replicates an index by definition. The degree of diversification may vary depending on the index. For instance, the Dow Jones Industrial Average has only 30 stock components compared to the S&P 500's more than 500, making the latter much less diversified.
Even if you own an S&P 500 index fund, your portfolio may not be sufficiently diversified if you don't also have modest allocations in low-correlation asset classes like bonds, commodities, real estate, and alternative investments, among others.
Can a Portfolio Be Over-Diversified?
Yes. Diversification objectives are not met if adding a new investment to a portfolio raises its overall risk and/or lowers its expected return (without appropriately lowering the risk). When a portfolio contains the ideal number of securities or when you add closely correlated securities, this "over-diversification" is more likely to occur.
Why Do I Need to Diversify?
Investors who diversify their portfolios avoid "putting all of their eggs in one basket." According to the theory, if one stock, industry, or asset class declines, others might increase. This is particularly true if the securities or assets held do not have a high degree of correlation. Diversification reduces the portfolio's overall risk mathematically without lowering the expected return.
What Goes Into A Diversified Portfolio?
A wide variety of investments should be included to diversify. For many years, financial advisors frequently advised creating a 60/40 portfolio, in which 60% of the capital would be invested in stocks, and 40% would be in fixed-income securities like bonds. Others, especially younger investors, have argued for greater stock exposure.
Conclusion
Owning a wide range of various stocks is one of the keys to a diversified portfolio. This entails holding various stocks from various sectors, including energy, healthcare, and technology. An investor doesn't need exposure to every industry; instead, they should concentrate on owning a wide range of top-notch businesses. Investors should also consider dividend stocks, growth stocks, value stocks, large-cap stocks, and small-cap stocks.
Investors should consider holding some non-correlated investments to a diversified stock portfolio (i.e., ones whose prices don't fluctuate daily with stock market indexes). Bonds, bank certificates of deposit, gold, virtual currencies, and real estate are some non-stock diversification options.
References
Understanding Portfolio Diversification from Fool.com
Investing in Southeast Asia can reward long-term investors looking for growth opportunities in emerging markets. However, finding quality and undervalued companies in this region is complex. Many challenges and risks are involved, such as political instability, currency fluctuations, corruption, and lack of transparency.
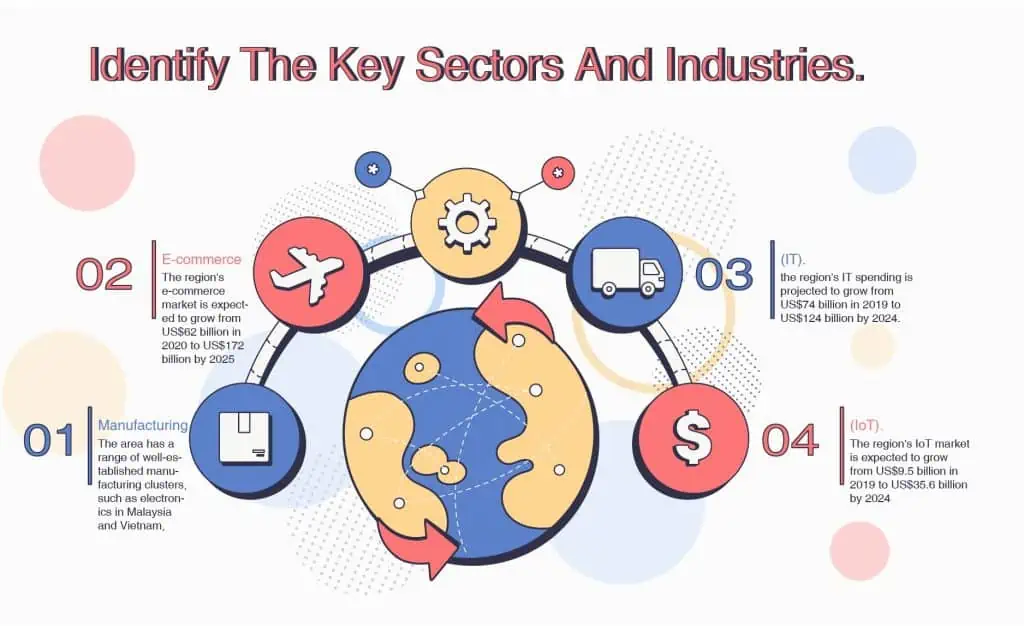
Identify the key sectors and industries.
Suppose you are looking for investment opportunities in Southeast Asia's fast-growing and diverse region. In that case, you might consider some quality and undervalued companies operating in critical sectors and industries that drive growth and innovation in the region, such as manufacturing, e-commerce, IT, IoT, and life sciences.
Manufacturing
Manufacturing is one of the most essential sectors in Southeast Asia, accounting for a large share of the region's GDP and exports. The area has a range of well-established manufacturing clusters, such as electronics in Malaysia and Vietnam, automobiles and packaged foods in Thailand, machinery and petrochemicals in Indonesia, and semiconductors, biopharmaceuticals, and aerospace components in Singapore. These clusters benefit from the region's large and growing market, extensive manufacturing base, new trade pact (the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership), and access to next-generation Industry 4.0 technologies. Some of the quality and undervalued companies in this sector include ARB Berhad, a Malaysian IT and IoT solutions and services company that ranked 72nd on the 2020 Asia Pacific Technology Fast 500 list, and vKirirom Pte. Ltd., a Singaporean software company that provides cloud-based solutions for education institutions.
E-commerce
E-commerce is another booming sector in Southeast Asia, as more consumers shop online for convenience, variety, and affordability. The region's e-commerce market is expected to grow from US$62 billion in 2020 to US$172 billion by 2025, according to a report by Google, Temasek, and Bain & Company. The region has several e-commerce platforms that cater to different segments and needs of online shoppers, such as Lazada, Shopee, Tokopedia, Bukalapak, Zalora, and Qoo10. Some quality and undervalued companies in this sector include PT Tokopedia, an Indonesian technology company specialising in e-commerce and ranked 94th on the 2020 Asia Pacific Technology Fast 500 list, and Involve Asia Technologies Sdn Bhd. This Malaysian media company connects e-commerce merchants with online publishers.
Information Technology(IT).
IT is another key sector in Southeast Asia, as more businesses adopt digital technologies to enhance their productivity, efficiency, and competitiveness. According to IDC, the region's IT spending is projected to grow from US$74 billion in 2019 to US$124 billion by 2024. The region has a vibrant IT ecosystem includes software developers, hardware manufacturers, cloud service providers, data analytics firms, cybersecurity experts, and digital transformation consultants. Some quality and undervalued companies in this sector include Blue Wireless Pte. Ltd. This Singaporean communications company provides wireless broadband solutions for enterprises across Asia Pacific and Africa, Cresco Data Pte. Ltd., a Singaporean software company that provides data automation and integration solutions for e-commerce businesses, Ivy Mobile Technologies Pte Ltd., a Singaporean software company that develops mobile applications for various industries, and PatSnap Pte. Ltd. This Singaporean software company provides intellectual property analytics and management solutions.
Internet of Things(IoT).
IoT is another emerging sector in Southeast Asia, as more devices and objects are connected to the internet to collect and exchange data. The region's IoT market is expected to grow from US$9.5 billion in 2019 to US$35.6 billion by 2024, according to Frost & Sullivan. The region has a solid potential to leverage IoT for various applications such as smart cities, manufacturing, agriculture, healthcare, transportation, and energy. Some of the quality and undervalued companies in this sector include Terminus Technologies.
Research the Leading Companies.
One of the most important skills for investors is to identify quality and undervalued companies that can generate consistent returns in the long term. In this article, we will share some tips on how to find such companies in Malaysia and Southeast Asia, a region with high growth potential and diverse opportunities.
Research the leading companies.
Research the leading companies you want to invest in each sector and their competitive advantages, such as market share, technology, customer base, and profitability. For example, in the e-commerce sector, you may want to look at companies like Shopee, Lazada, and Tokopedia, which have strong brand recognition, user loyalty, and network effects. In the banking sector, you may want to look at companies like Maybank, DBS, and CIMB, which have large customer deposits, digital innovation, and regional presence.
Analyze the financial performance.
You can use various metrics and ratios to assess the quality and undervalued aspects of the companies, such as earnings growth, return on equity, dividend yield, price-to-earnings ratio, and price-to-book ratio. You can also compare these metrics with their peers and industry averages to understand their relative value.
Evaluate the prospects and risks.
You can use various sources of information to gather insights and opinions on the companies, such as annual reports, analyst reports, news articles, podcasts, and forums. You can also consider the macroeconomic factors and trends that may affect the companies, such as interest rates, inflation, currency fluctuations, consumer behaviour, and regulations.
Following these steps, you can find quality and undervalued companies to invest in in Malaysia and Southeast Asia. However, you should also do your due diligence and research before making investment decisions. Investing involves risks and uncertainties; you should be prepared for possible outcomes.
Evaluate each company's financial performance and valuation.
Clear investment objective and strategy.
What are your investment goals, risk tolerance, time horizon, and preferred sectors or industries? This will help you narrow your search and focus on the most relevant companies for your portfolio.
Some market research and analysis.
What are the macroeconomic trends, political risks, regulatory environment, and competitive landscape in Malaysia and Southeast Asia? How do these factors affect different sectors and industries' growth prospects and profitability? You can use various sources of information, such as news articles, reports, databases, and websites, to get a comprehensive overview of the market conditions and opportunities.
Screen and select potential companies based on your investment criteria
You can use various tools and platforms, such as stock screeners, financial websites, and online investors, to filter and sort companies based on various parameters, such as market capitalization, sector, industry, dividend yield, growth rate, etc. You can also use qualitative factors, such as management quality, competitive advantage, brand recognition, customer loyalty, etc., to assess each company's potential.
Using multiple metrics to evaluate.
Evaluate each company's financial performance and valuation using revenue growth, earnings per share, return on equity, price-to-earnings ratio, and market capitalization. These metrics will help you measure how well the company generates income and creates value for its shareholders. You can compare these metrics with the industry averages and historical trends to determine if the company is overvalued or undervalued. You can also use other valuation methods, such as discounted cash flow analysis, relative valuation, or intrinsic value estimation, to estimate the fair value of each company.
Investment decision based on your analysis and judgment.
You should consider both the potential returns and risks of each investment opportunity. You should also diversify your portfolio across different sectors, industries, countries, and regions to reduce exposure to specific risks and enhance your overall performance. You should also monitor your portfolio regularly and adjust your strategy based on your investments' changing market conditions and performance.
Compare the valuation of each company.
One of the most important skills for investors is identifying quality and undervalued companies in the market they want to invest in. Quality companies have substantial competitive advantages, consistent profitability, high returns on capital, and good growth prospects. Undervalued companies trade below their intrinsic value, meaning the market has not fully recognized their potential.
One way to find quality and undervalued companies in Malaysia and Southeast Asia is to compare the valuation of each company with its peers and the industry average, looking for signs of undervaluation or overvaluation. Valuation estimates a company is worth based on its financial performance and future prospects. There are various valuation methods and metrics that can be used, such as price-to-earnings ratio (P/E), price-to-book value ratio (P/B), price-to-sales ratio (P/S), price-to-cash flow ratio (P/CF), dividend yield, earnings growth rate, return on equity (ROE), and free cash flow yield.
By comparing the valuation of each company with its peers and the industry average, investors can get a sense of whether a company is cheap or expensive relative to its competitors and the market. For example, suppose a company has a lower P/E ratio than its peers and the industry average. In that case, it may indicate that the company is undervalued, which generates more earnings per share than the market is willing to pay. Conversely, suppose a company has a higher P/E ratio than its peers and the industry average. In that case, it may indicate that the company is overvalued, generating less earnings per share than the market expects.
However, valuation is not an exact science. Many factors can affect the valuation of a company, such as its growth prospects, competitive position, risk profile, capital structure, accounting policies, and market sentiment. Therefore, investors should not rely solely on valuation metrics to make investment decisions but also consider other aspects of a company's business model, strategy, financial performance, and future outlook. Additionally, investors should be aware of the limitations and assumptions of each valuation method and metric and use them with caution and common sense.
Conduct due diligence
Company's management team
You want to look for leaders with relevant experience, vision, and integrity and align with shareholders' interests. You can check their backgrounds, track records, reputations, and incentives. You can also assess their communication, strategic thinking, and decision-making abilities.
Evaluate the company's business model.
You want to understand how the company creates value for its customers, suppliers, partners, and shareholders. You can analyze its products or services, target markets, competitive advantages, revenue streams, cost structure, and profitability. You can also examine its innovation capabilities, customer loyalty, and market share.
Examine the company's growth strategy.
The third step is to You want to see how the company plans to expand its business in the future, both organically and inorganically. You can review its goals, objectives, milestones, and action plans. You can also consider its opportunities and threats in the external environment, such as industry trends, customer preferences, regulatory changes, and competitive forces.
Identify the company's risks and challenges.
You want to know the potential pitfalls and uncertainties that could affect the company's performance and valuation. You can evaluate its financial health, operational efficiency, risk management practices, and contingency plans. You can also monitor its performance indicators, such as revenue growth, earnings per share, return on equity, and free cash flow.
Estimate the company's intrinsic value.
You want to compare the company's current market price with its fair value based on future cash flows. You can use various valuation methods, such as discounted cash flow analysis, multiples analysis, dividend discount model, or residual income model. You can also adjust your valuation for different scenarios and assumptions.
Invest in companies that have strong fundamentals.
Quality companies have strong fundamentals, such as solid balance sheets, competitive advantages, loyal customers, and proactive management. These companies can withstand market fluctuations and deliver sustainable growth and profitability over time. Undervalued companies have an attractive valuation, meaning their current share price does not reflect their true worth or future potential. These companies are often overlooked or misunderstood by the market, creating a margin of safety for investors who can recognize their value.
To find quality and undervalued companies in Malaysia and Southeast Asia, we need to adopt a bottom-up approach, focusing on each company's characteristics and performance rather than the macroeconomic factors or industry trends. This requires us to do thorough research and analysis of the company's financial statements, business model, competitive landscape, growth prospects, risks, and valuation. We also need to monitor the company's news and developments regularly and be alert for any changes affecting its outlook.
Some of the criteria that we can use to screen for quality and undervalued companies are:

Return on equity (ROE).
This measures how efficiently a company uses its shareholders' equity to generate profits. A high ROE indicates that the company has a strong competitive edge and can reinvest its earnings to grow its business. We can look for companies with an ROE of at least 15% or higher than their industry average.
Earnings growth.
This measures how fast a company's earnings are increasing over time. A high earnings growth indicates that the company has a high growth potential and can increase its market share and profitability. We can look for companies with an earnings growth of at least 10% or higher than their industry average.
Price-to-earnings ratio (P/E).
This measures how much investors will pay for each unit of a company's earnings. A low P/E indicates that the company is undervalued or has a low expectation from the market. We can look for companies with a P/E of less than 15 or lower than their industry average.
Dividend yield.
This measures how much a company pays out in dividends relative to its share price. A high dividend yield indicates that the company rewards its shareholders with consistent and generous payouts. We can look for companies with a dividend yield of at least 3% or higher than their industry average.
Conclusion
In conclusion, finding quality and undervalued companies to invest in Southeast Asia can reward long-term investors. However, it requires careful research, patience, and discipline to avoid falling into value traps or missing out on growth opportunities. Some metrics that can help investors identify undervalued companies are the price-to-earnings ratio, price-to-book ratio, and price/earnings-growth ratio. These metrics can help compare companies across different industries and markets and reveal their intrinsic value relative to their current price. By applying these metrics, investors can build a diversified portfolio of value stocks with strong fundamentals, attractive valuations, and potential for future growth.
Reference
Opportunities for companies in Southeast Asia to reimagine
Investing in Southeast Asia: What’s Behind the Boom
How to Find Undervalued Companies
Updated 29/8/2022
Startup valuations reveal a company's ability to employ new cash to expand, exceed consumer and investor expectations, and achieve the next goal. Unicorn valuations, or companies worth $1 billion or more, now number in the hundreds. There are now "decacorns," or startups worth $10 billion or more, as well as "hectocorns," or companies worth more than $100 billion.
These calculations, while remarkable, aren't as objective as you may believe. A startup valuation may take into account your team's experience, product, assets, business model, total addressable market, competition performance, market opportunity, goodwill, and other criteria.
What Is Startup Valuation?
For any corporation, valuing its assets is never simple. The task of assigning a valuation to businesses with little or no revenue or profits and uncertain futures is extremely difficult. It's usually a matter of valuing mature, publicly-traded businesses with consistent revenues and earnings as a multiple of their earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortisation (EBITDA) or based on other industry-specific multiples.
However, valuing a new enterprise that isn't publicly traded and may be years away from sales is much more difficult. There are numerous factors to examine, including the management team and industry trends, as well as product demand and marketing hazards.
Important Factors For Pre-Revenue Starup Valuation
The majority of the time, early-stage firms are valued in the middle, which means that founders don't get as much as they expected and investors may invest higher than they intended. Here are some major elements to consider when valuing a startup before it generates income.
Traction Is Demostration Of Concept
If you are trying to figure out how to value a firm with no income, one of the most important factors to consider is traction. e
- Number of Users. Demonstrating that you already have clients is critical. The greater the number, the better.
- Marketing Effectiveness. If you can demonstate that you can recruit high-value consumers for a low acquisition cost, you will draw the interest of pre-revenue investors
- Growth Rate. Demonstrating that your business has expanded on a limited budget is advantageous, since many investors will see the potential for expansion if you have some funding.
There is a link between these three ideas, as a strong marketing plan will result in significant growth. When that happens, the number of users will skyrocket. As a result, you automatically add value to your startup by demonstrating that you have a solid, scalable business idea. Investors will begin to view their money as fuel for the fire.
The Importance Of A Founders' Team
Pre-revenue investors want to know that they are investing in a team that's going to be successful. They will think about the following:
- Proven Experience - A startup with personnel who have had previous success with other startups will be more appealing than one with inexperienced first-timers.
- Skills Diversity - A startup team should ideally consist of a mix of professionals with complementary skills. A brillant programmer cannot do everything on her own, but when she joins forces with a marketing expert, the startup becomes more valuable.
- Commitment - Great individuals are simple one piece of the puzzle. Those individuals must have the time and commitment to ensure the startup's success. A team of part-time workers will not be appealing.
Prototypes / Minimum Viable Product (MVP)
A prototype is a game-changing addition, regardless of which pre-money valuation method you choose. Being able to display a functioning model of your product to pre-revenue investors not only demonstrates your persistence and vision for turning ideas into reality but also accelerates the business's launch date.
If you have a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) and some early users, you might be able to raise $500k to $1.5M in funding. If your company is evaluated using the valuation-by-stage method, which is utilised by many venture capitalists and angel investors, a working prototype could fetch you even more money. This might result in a $2 million to $5 million investment.
Demand and Supply
Your startup valuation will be impacted if you operate in a market where the number of business owners outnumbers the number of willing investors. Many business owners are desperate for investment in such a competitive environment, and may even sell themselves short to do so.
On the other hand, you have a unique patented idea for a startup that is causing a stir in the industry. This may increase investor demand, increasing the value of your firm.
Hot Trends and Emerging Industries
Many investors will be prepared to pay a premium in booming businesses like Artificial Intelligent (AI) or mobile gaming. The internet age is rife with prospects that many regards as "the next great thing," so if your startup is in the proper field, it could be worth more.
High Margins
Investors aren't interested in high-margin products with low-profit margins. A high-growth business, on the other hand, with good margins and excellent revenue growth estimates, may be able to attract greater financing.
Common Startup Valuation Method
It may seem difficult to perform a pre-revenue business valuation on your own, but you may benefit from the knowledge and wisdom of other entrepreneurs, angel investors, and venture capitalists. Furthermore, by familiarizing yourself with the most common startup valuation methods, you will not only be able to analyze a firm with no revenue but you will also be able to negotiate a better deal with pre-revenue investors.
The Berkus Method
Investors, according to angel investor Dave Berkus, should be able to see the company reaching $20 million in five years. His approach evaluates five key components of a startup.
- Concept. The product provides basic value while posing a manageable risk
- Prototype. This lowers the danger of technology failure.
- Quality Assurance. If it isnts already in place, the startup intends to hire a quality assurance staff
- Connections. There are already some strategic partnerships in place, which lessens market competitive threats.
- Launch Plan. There is some evidence of sales strategy and preparation for product launch. (Note that this does not apply to all pre-revenue businesses)
Each facet is assigned a grade of up to $500,000, implying a maximum valuation of $2.5 million. The Berkus Method is a straightforward estimating technique popular among software firms. It is a good technique to estimate worth, but it lacks the flexibility that some people want because it doesn't consider that market.

Scorecard Valuation Method
Another option for pre-revenue enterprises is the Scorecard Valuation Method. It also compares startups to companies that have already received funding, but with additional criteria.
To begin, first, determine the average pre-money valuation of comparable businesses. Then look at how your company compares to the traits listed below. After that, assign a comparison percentage to each quality. When compared to your competition, you can be on par (100%), below average (<100%), or above average (>100%) for each characteristic.
| Criteria | Weight | Target Company | Factor |
| Team | 30% | x | = 0.3*x |
| Size Of The Opportunity | 25% | x | = 0.24*x |
| Product/Technology | 15% | x | = 0.15*x |
| Competitive Environment | 10% | x | = 0.10*x |
| Sales/Marketing | 10% | x | = 0.10*x |
| Need For More Financing | 5% | x | = 0.05*x |
| Other | 5% | x | = 0.05*x |
| Total | Sum of all factors |
For example, you give your e-commerce team a 150% score since it's complete, well-trained, and staffed with experienced developers and marketers, some of whom have previously worked for competitors. To get a factor of 0.45, multiply 30% by 150%.
Calculate the sum of all factors for each startup quality. To calculate your pre-revenue valuation, multiply that sum by the typical valuation in your industry.
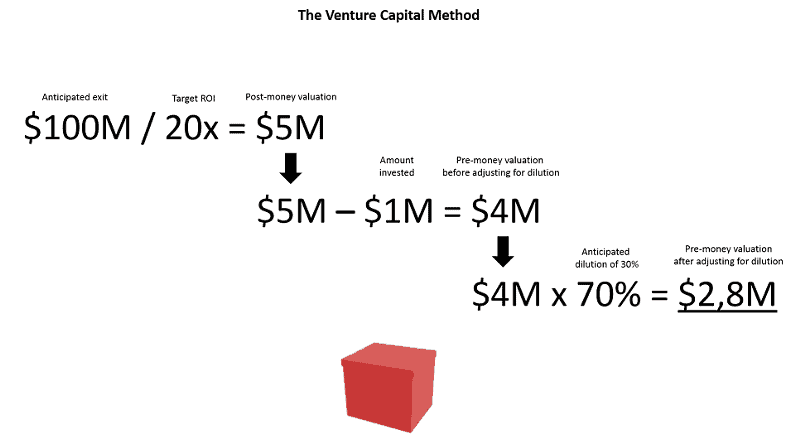
Venture Capital (VC) Method
The venture capital approach was popularised by Harvard Business School Professor Bill Sahlman. The venture capital technique is a two-step procedure that necessitates the use of a number of pre-money valuation algorithms.
First, determine the business's terminal value in the harvest year. Second, determine the pre-money valuation by working backwards from the predicted return on investment (ROI) and investment amount. The harvest year is the year in which an investor will depart the firm. Terminal value is the estimated value of the startup at a specific point in the future. The Industry Price-Earning Ratio (P/E ratio), or stock price-to-earnings ratio, is another phrase you will need to grasp. A P/E ratio of three, for example, suggests that the stock is worth three times its earnings.
Calculating Terminal Value
To calculate the terminal value, the following figures are required.
- Estimated revenue for the harvest season
- Profit margn forecasted for the harvest year
- P/E ratio of the industry
You may uncover industry averages for the P/E ratio and predicted profit margins by doing some research online. Once you have gathered your data, perform the following calculation:
- Terminal Value = earnings x P/E
For example, in five years, a tech company expects to generate $10 million in revenue, with a 10% profit margin. The P/E ratio is 20. As a result, the terminal value is $10 million multiplied by 10% and multiplied by 20 to equal $20 million.
Calculating The Pre-Money Valuation
The following items are required for the second step.
- Required Return On Investmetn (ROI)
- Investment Amount
Then calculate it based on the formula below.
Pre-Money Valuation = Terminal value/ROI - Investment amount
Imagine a pre-revenue investor is looking for a 10x return on his $1 million investment.
Pre-Money Valuation = $20M/10 - $1M = $1M in this scenario.
We may calculate the current pre-revenue startup valuation to be $1 million using this method. With a $1 million investment and reasonable growth and industry profits estimates, the company may be worth $20 million in five years.
Risk Factor Summation Method
This approach combines elements of the Scorecard Method and the Berkus Method to produce a more precise evaluation of an investment's risk. It takes into account the following risk:
- Management
- Stage of the Company
- Capital/Funding Risk
- Manufacturing Dangers
- Technology Risk
- Risks in Sales and Marketing
- Threat of Competition
- Political/Legislation Risk
- Litigation Risk
- International Risk
- Risk to One's Reputation
- Potential Lucrative Risk
Each of these risk areas will be given a score based on the following criteria:
- - 2 (-$500,000) - Extremely Negative
- - 1 (-$250,000) - Negative for scaling the startup and carrying out a successful exit
- 0 ($0) - Neutral
- + 1 ($250,000) - Positive
- + 2 ($500,000) - Excellent for scaling the business and execiting a successful exit
The pre-revenue company valuation will increase by $250,000 for every +1 and by $500,000 for every +2. For every -1, the pre-revenue value drops by $250,000 and for every - 2, it drops by $500,000.
This method is useful for assessing the risks that must be addressed in order to achieve a successful exit, and it can be combined with the Scorecard Method to provide a comprehensive assessment of the startup's value.
Comparable Transactions Method
Because it is based on precedent, the Comparable Transactions Method is one of the most common startup valuation methodologies. You're responding to the question, "How much did startups like mine cost to acquire?"
Consider the case of Rapid, a fictional shipping firm that was purchased for $24 million. It had 700,000 subscribers on its mobile app and website. That works out to about $34 per user. Your shipping company has a user base of 120,000 people. This gives your company a market value of around $4 million.
You can also look up revenue multiples for companies in your industry that are similar to yours. It's possible that SaaS companies in your market produce 5x to 7x the prior year's net sales.
You must include ratios or multipliers in any comparison model for everything that is significantly different between your two businesses. If another SaaS company has proprietary technology and you don't, for example, you might want to choose a multiplier on the lower end of the spectrum, such as 5x (or lower) in our example.
Cost To Duplicate Approach
This strategy involves evaluating the firm's tangible assets before calculating how much it would cost to replicate the startup elsewhere. When looking for pre-revenue investors, it's helpful to remember that no wise investor will invest more than the assets' market value.
A tech startup, for example, might think about the costs of producing their prototype, patent protection, and research and development. Unfortunately, this strategy does not account for future possibilities, nor does it incorporate intangible assets such as brand value or current market hot trends.
As a result, because it is such an objective approach, it is best utilised to acquire a lowball estimate of a startup's pre-revenue worth.
Conclusion
You must balance all of the things that your startup must supply in order to present yourself with the highest valuation for your pre-revenue business. Before approaching individuals who might be interested in investing in your company, it is equally critical that you, as the owner, learn how to value it.
Experimenting with different valuation methodologies will allow you to show your investors that your company has the ability to grow and is worth their money.
Reference
Understanding Startup Valuation
Unicorn firms are those companies that attain a $1 billion value without being listed on the stock market, and they are every tech startup's goal. What elements contribute to the success of these businesses? Which are the most valuable in the world? What are the pros and cons of investing in one? We address these and other concerns in the sections that follow.
The Origin of the Term "Unicorn Company"
The name was coined in 2013 by venture capitalist Aileen Lee to emphasise the rarity of such enterprises at the time. Lee sorted over 60,000 software and internet firms that received funding between 2003 and 2013, discovering that just 39 startups were valued at more than $1 billion, making them exceptionally exclusive and opportune investments.
Unicorn companies have grown far less common over the years. Although reaching unicorn status is more frequent today than ever before, these $1 billion+ post-money values are still tremendously astounding. Unicorn businesses are being scrutinised and reported on by individuals with an interest in the most prominent participants in the private markets.
What Kind of Companies Make Unicorns?
Entrepreneurs always wonder about the keys to becoming the next unicorn but constructing a road map for creating a unicorn company is a difficult task. Many factors are involved in the success or failure of a startup, but, in the absence of miracle formulae, it is nevertheless possible to provide a series of common pointers:
Social media are a great ally
They use social media platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram to spread their message. Because of segmentation, businesses are able to amplify their message and impact their target demographic for a much lower investment.
The customers are always at the fore
They use a customer-centric business strategy. In other words, they consider the consumer before, during, and after throughout the customer's journey. The importance of user experience is one of the keys to success. In the past, the focus was only on the product. However, the purchasing experience is now equally or even more crucial.
Global and rapid expansion
Good businesses start with a global mindset and follow a get big fast strategy in order to, as the name suggests, get big as quickly as possible. Going all-in on internationalisation and having a scalable model is critical to attaining both of these goals.
Wide-ranging team
Unicorn companies are multidisciplinary and cross-cultural organisations. As a result, they have a highly diverse professional profile, which is one of their assets when it comes to developing new ideas. Furthermore, they are young companies that value talent and creativity.
Uncertainty is part of the daily routine
The distinction between success and failure is razor-thin. Because these companies are fully aware of this, they learn to take the rough with the smooth and develop a special resilience.
How Many Unicorns Companies Are There?
In 2019, there were 354 active unicorn firms worldwide, up from 348 the previous year. There were 439 active unicorn firms by the end of 2019, including 139 new startups. In 2020, 162 new firms gained unicorn status throughout the world, bringing the total number of active unicorn companies to 538. In 2021, there were 355 new unicorn firms, and the year finished with 537 active companies, about the same as the previous year.
According to CB Insights, the globe had 1,068 unicorn enterprises as of March 30, 2022. 519 of these privately held firms valued at $1 billion or more were "born" in 2021 alone. The worldwide unicorn herd surpassed 1,000 at the start of the current year.
Why Are There So Many Unicorn Companies Emerging?
One factor for the explosion of unicorn companies is the growing convergence of the private and public markets. Historically, corporations depended on initial public offerings (IPOs) to raise financing to grow operations. Today, companies may now raise higher sums of private capital early on, allowing them to attain billion-dollar valuations without going public.
The Most Valuable Unicorn Businesses
Unicorns are rare and difficult to come by. Something similar occurs in these types of startups. Below, we list the 5 most highly valued:
- Uber: mobile taxi app
- WeWork: job sharing company
- Airbnb: holiday & tourist accommodation platform
- Stripe: a company that allows individuals and businesses to receive payments via the Internet.
- Epic Games: video games company
Advantages & Disadvantages of Investing in Unicorns
Investing in a unicorn firm, like any other investment, has advantages and disadvantages.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| You Likely Know the Company | Billion-Dollar Valuations Don’t Necessarily Mean Profits |
| Some Unicorns Really Do Fly | Ridiculous Overvaluations |
| Innovation Has Long-Term Value | Lack of History |
Advantages of Investing in Unicorns
Investing in unicorn firms has various advantages which include:
You likely know the company. Unicorn firms don't reach billion-dollar valuations before going public for no reason. These businesses have produced something really unique. If they have a product on the market, it is most certainly a very popular one. If it hasn't yet entered the market, a huge portion of the population is probably aware that it is on the way. Investing in firms you've heard of and are familiar with has a strategic advantage. Remember that intelligent investment increases the investor's chances of witnessing growth.
Some unicorns really do fly. Some unicorn firms, like their mythological counterparts, soar after their initial public offering. Zoom is an excellent example of a successful unicorn firm. The stock debuted in 2019 at a low price of $36 per share. After a year, the stock was trading much above $100 per share, momentarily exceeding $500 per share in late 2020. Even after major consolidation, the corporation is now valued at well over $40 billion, with shares trading in the triple digits.
Innovation has long-term value. Unicorn firms are the kings of innovation, and their worth is enormous. Those who do strike tend to hit hard, resulting in massive long-term rewards. Consider the case of Tesla. Since its IPO at $17 per share in 2010, the stock has never gone below its IPO price. After only 11 years, the stock is now worth approximately $1,000 per share.
Disadvantages of Investing in Unicorns
While there are several obvious advantages to investing in unicorn companies, even the most beautiful rose has thorns. When investing in these equities, there are a few downsides to consider.
Billion-dollar valuations don't necessarily mean profits. Although all unicorn firms have a valuation of $1 billion or greater, many of them lack one key component: earnings. Consider Uber, which has a market capitalization of more than $65 billion. However, it has yet to make a single profit. Every quarter, the corporation loses millions of dollars. Many other unicorn firms follow suit, making them riskier investments. After all, a corporation that is losing money will ultimately run out of money.
Ridiculous overvaluations. In general, unicorn firms are valued differently than others in their industry. As a result, when looking at basic valuation criteria like price-to-sales or price-to-book value, these firms are often overvalued. That is, when you invest in a unicorn firm, you are betting on the company being enormously successful and expanding at a significantly higher rate than the typical company in its field. That might be a hazardous bet to make.
Lack of history. The billion-dollar value of a unicorn firm comes from venture capitalists and institutions that invest in it early on. However, because these firms are pre-IPO, the market hasn't had a chance to price them. Often, the market does not feel the firm is as valuable as institutions do, resulting in a drop after the shares are listed on the public stock exchange. However, without a trading history, it is impossible to predict how the broader market will value the firm.
Conclusion
Unicorn stocks are fascinating. These firms develop technology or services that are so far ahead of their time that they have the potential to alter the whole industry in which they operate. As a result, they fly to billion-dollar valuations well ahead of their peers.
There is, however, a catch. Unicorns in the market, unlike the mythological animals after whom they are called, are not all flawless and lovely. While some have the ability to yield substantial returns, others have the potential to cause substantial losses.
So, instead of making a FOMO (fear of missing out)-driven move, if you're thinking about investing in these companies, do your homework and critically assess if the technology that keeps the unicorn's ticker ticking is something you believe to be revolutionary. Dive into the company's accounts and make an informed judgement whether the company’s billion-dollar valuation is justified.
References
Do startups dream of unicorns?
Global Unicorn Herd Now Counts 1,000+ Companies
What Is a Unicorn Company and Should You Invest in a Startup Business?
Many people automatically think of profit when they are asked how well a company is doing financially. However, profit might signify different things depending on what factors are used while determining it. A failed business is one that does not make a profit, regardless of how many clients it has.
The startups, on the other hand, do not necessarily highlight profitability. Indeed, many firms are acquired or go public years later without ever generating profit. This grow-big strategy is not possible for self-funded startups unless they are producing enough money to sustainably fuel expansion.
Irrespective of how you choose to create your company, the leading criteria for every business is achieving a healthy return on investment (ROI) in your startup. So, why you should focus on your return on investment in your startup?
What is Return on Investment?

Return on investment (ROI) is a performance metric that is used to assess the efficiency or profitability of an investment or to compare the efficiency of many investments. ROI attempts to directly assess the amount of return on a certain investment in relation to the cost of the investment. In short, when you make investments into an investment or a company venture, ROI helps you comprehend how much profit or loss your investment has generated.
Return on investment may be conceived of in four different ways, depending on the observer's viewpoint and objectives.
An Investor
From the point of view of an investor, such as an angel investor, who effectively lends money to the company. In all circumstances, investors anticipate a return on their investment, which is generally in the form of interest or dividends.
The money allotted by the organisation to finance the interest and any other agreed-upon payments to investors is indicated as an expenditure on the cash flow statement and is commonly referred to as a return on investment.
Organisation Itself Is An Investor
When the organisation itself is an investor, lending money to other organisations and/or investing its own cash in interest-bearing bank accounts. The interest earned is also included as a receipt in the ROI section of the cash flow statement.
Performance Of The Organization's Investments In Capital Equipment
The performance of the organization's investments in capital equipment such as plants and property. Obviously, an organisation hopes to generate money as a reward for these investments, and the return on capital employed (ROCE) is a measure of its performance. ROCE is one of the financial statistics that are important in assessing return on investment.
Comparative Return On Investment
Last but not least, the issue of comparative return on investment arises during the consideration of capital investment options. There are several approaches for evaluating the relative advantages of various capital investments.
How do you calculate ROI?
There are several methods to determine ROI, one is to divide net profit by total assets, then, multiplied by 100.

The other is by subtracting the initial value of the investment from the final value of the investment (which equals the net return), then dividing this new number (the net return) by the cost of the investment, then finally, multiplying it by 100.

Since it is stated as a percentage, it is possible to compare the efficacy or profitability of various investment options. It is closely connected to metrics such as return on assets (ROA) and return on equity (ROE).
However, while evaluating ROI, additional aspects that may be less prominent, such as time, hidden expenses and fees, and even emotional ones such as stress, must be included. All of these factors might have a big influence on your ROI.
Advantages and Disadvantages of ROI
Here are some advantages and disadvantages that Return of Investment (ROI) can bring:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| A better measurement of profitability | Profit is subjective |
| Minimize conflict of interest and achieve goal congruence | Might be incomparable with other companies |
| Acting as a comparative analysis | Encourage management to invest in a short-term project and discourage them from making new investments |
| Breakdown segment or division performance | The time factor is omitted |
Advantages Of ROI
A better measurement of profitability
ROI ties net income to divisional investments, providing a more accurate measure of divisional profitability. All divisional managers are aware that their performance will be reviewed based on how they used assets to generate a profit; this encourages them to make the best use of assets.
It also guarantees that assets are only bought when they are certain to provide profits in accordance with the organization's policy. As a result, the primary focus of ROI is on the needed amount of investment. A cost-benefit analysis of this sort assists managers in determining the rate of return that could be expected from various investment options.
This enables them to select an investment that will improve both divisional and organisational profit performance while also allowing them to make better use of current investments.
Minimize conflict of interest and achieve goal congruence
The greater the interest rate, the larger the company's return. Using it as a tool to analyse investment ideas ensures that management will operate in the best interests of the company. It helps to ensure that both the company and its managers have the same goal in mind: to enhance shareholder value.
As a result, ROI guarantees goal congruence among the various divisions and the company. Any rise in divisional ROI will result in an increase in the overall ROI of the company.
Acting as a comparative analysis
ROI may also be used to compare the profitability and asset utilisation of different business divisions. It can be utilised for inter-firm comparisons if the businesses whose results are being compared are of comparable size and in the same industry, where the management will be able to benchmark the ratio in the market. ROI is a useful metric since it can be easily compared to the associated cost of capital when deciding on investment options.
Breakdown segment or division performance
Using ROI allows the organisation to examine the performance of a division or area. Based on the prospective earnings or growth, they will be able to determine whether to sell or extend the operation of such business units.
From an investment perspective, ROI is important in assessing performance which focuses on maximising profits and making sound judgments about the acquisition and disposal of capital assets.
Disadvantages Of ROI
Accounting profit can be very subjective
Profit can be manipulated by accounting policy and management judgment as they can reduce depreciation expenses by establishing an extended usable life in order to increase profit. Other than that, they will grant a lower allowance for the bad debt even if it is not reasonable.
Might be incomparable with other companies
It will also be challenging to compare ROI with other companies due to variances in accounting policy in each organisation. As we can see from the preceding statement, profit might vary depending on the firm. It is the same as investment cost, and some may use original investment, but others may use net book value, fair value, and so on.
Encourage management to invest in a short-term project and discourage them from making new investments
Only short-term ROI will have an influence on their current performance, whereas long-term projects take too long to provide results. Thus, there will be a higher chance that the management will sacrifice the company’s long-term benefits even if certain projects generate higher returns.
The same goes for when new investments are made, the current ROI will decrease investment in a new IT system, fixed asset, factory, and product line will unlikely generate profit in the short term. However, if we do not complete them on time, the company would face a significant problem that will even impact the company.
The time factor is omitted
When calculating ROI, each project term is completely discarded in favour of focusing solely on the return. It will take a longer period of time to archive a greater return. When the time value of money is considered, a highly profitable enterprise may turn out to be less profitable.
How Do You Use ROI in Your Business?
ROI calculation provides several benefits, but how? What is the first and most obvious? Understanding the impact of your investment on your business. If you discover that you are spending money on an expense, it is obvious that something has to be changed. Many different forms of ROI may assist you in making key business choices, including, but not limited to:
- Purchasing a new asset: Adding new tools, equipment, and goods to your business may be a good thing, but they must be chosen intelligently. Determining the ROI on an equipment purchase enables you to ascertain the cost of your new item and what sorts of equipment to invest in in the future.
- Hiring new staff: Is your new staff improving or lowering the profitability of your company? Monitoring your staff's ROI will help you better identify the kind of individuals to employ (or fire).
- Having a new department: Adding a new department to your company, like employing new staff, may be wise if it helps raise profitability. You might not want to make assumptions here; compute return on investment to measure the profitability of your departments and uncover chances for improvement.
- Sales strategies: Did a certain tactic contribute to a sale? Tracking which kind of sales methods produce results will offer you an idea of how to enhance your company's profitability.
Conclusion
Know your figures since utilising ROI to evaluate an investment is a fine place to start, but don't stop there. Even though companies at the idea stage might be unpredictable, keep in mind that development is the accumulation of modest moves ahead.
You can safely gauge your progress and the needed investment when you focus on a few steps at a time. However, ROI cannot be the only indicator used by investors to make decisions because it does not account for risk or time horizon and necessitates a precise measurement of all expenses.
References
An investment in an initial public offering (IPO) has the potential to provide substantial profits. Prior to investing, however, it is critical to understand how the process of trading these assets differs from typical stock trading, as well as the unique risks and laws involved with IPO investments. In this article, we will be diving deeper into the understanding of IPO.
Definition of an Initial Public Offering (IPO)
An IPO, or initial public offering, is the procedure through which a private firm issues shares of stock to investors for the first time. When a firm goes public via an IPO, we frequently refer to it as "going public."
Companies that are just getting started or those that have been in business for decades might choose to go public through an IPO. The IPO process enables a firm to generate funds to support operations, accelerate expansion, and pay down debt. An IPO also allows corporations to repay its investors, who have the option of selling their private shares in the IPO. In general, a private firm with significant development potential will explore going public, mostly for the reasons stated above. It's the obvious and expected next step for successful companies in many respects. Airbnb, which went public in the winter of 2020, is one of the more high-profile recent examples of a firm going public.
After a firm decides to "go public," it selects a lead underwriter to assist with the securities registration procedure and the distribution of shares to the public in an IPO. The lead underwriter then assembles a syndicate of investment banks and broker-dealers to sell IPO shares to institutional and individual investors.
How an IPO works?
A corporation is deemed private prior to an IPO. As a pre-IPO private company, the firm has grown with a limited number of shareholders, including early investors such as the founders, family, and friends, as well as professional investors such as venture capitalists or angel investors.
An IPO is a significant milestone for a company since it allows it to raise a large sum of money. This increases the company's capacity to develop and expand. The enhanced openness and share listing credibility may also aid in obtaining better terms when seeking borrowed capital.
When a firm thinks it is mature enough for the rigours of Securities and Exchange Commission Rules and Regulations (SEC), as well as the rewards and obligations of public shareholders, it will begin to promote its interest in going public.
This stage of development is often achieved when a firm has attained a private valuation of about $1 billion, sometimes known as unicorn status. However, depending on market competition and their capacity to fulfil listing standards, private firms at varied valuations with good fundamentals and demonstrated profitability potential can potentially qualify for an IPO.
Underwriting due diligence is used to price a company's IPO shares. When a corporation goes public, previously owned private share ownership transitions to public ownership, and current private shareholders' shares are worth the public selling price. Special arrangements for private to public share ownership can also be included in share underwriting.
Meanwhile, the public market provides a large chance for millions of investors to acquire shares in a firm and contribute cash to the shareholders' equity of a corporation. Any individual or institutional investor interested in investing in the firm is considered a member of the public.
Overview of IPO Steps
Here are some steps a company must undertake to go public via an IPO process:
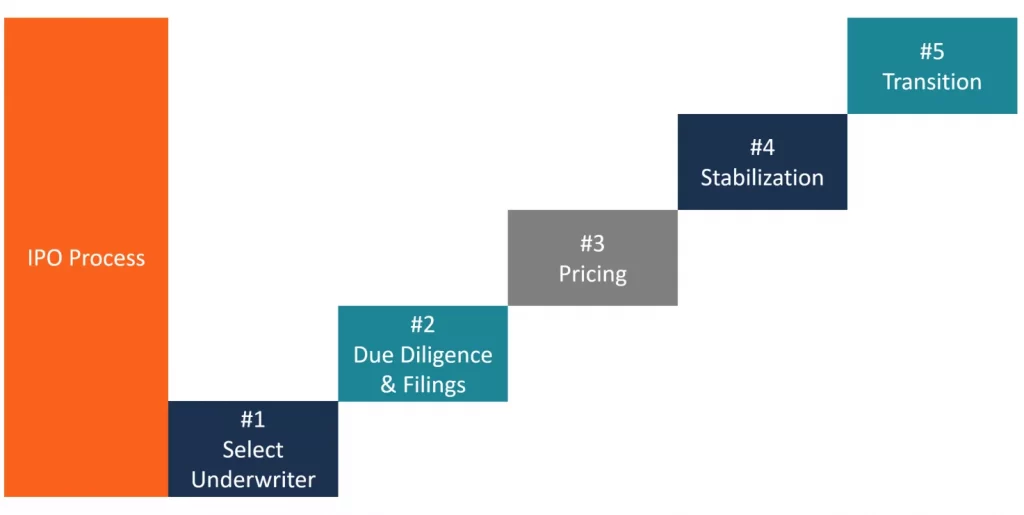
Select an Investment Bank
The issuing company's first stage in the IPO process is to select an investment bank to advise it on its IPO and offer underwriting services. The investment bank is chosen based on the following criteria:
- Reputation
- The quality of research
- Industry expertise
- Distribution, i.e., if the investment bank can provide the issued securities to more institutional investors or to more individual investors
- Prior relationship with the investment bank
Due dilligence and regulatory filings
Underwriting is the procedure through which an investment bank (the underwriter) serves as a middleman between the issuing firm and the investing public in order to assist the issuing company in selling its initial set of shares. The issuing business can choose from the following underwriting options:
- Firm Commitment: In such a case, the underwriter buys the whole offer and resells the shares to the investing public. The firm commitment underwriting structure ensures that a specific amount of money will be obtained for the issuing business.
- Best Efforts Agreement: The underwriter does not guarantee the amount raised for the issuing business under such an arrangement. It solely sells securities on the company's behalf.
- All or None Agreement: The offering is cancelled unless all of the offered shares are sold.
- Syndicate of Underwriters: Public offers can be managed alone by one underwriter or by numerous managers (shared management). When numerous managers are present, one investment bank is designated as the main or book-running manager. The lead investment bank develops a syndicate of underwriters by developing strategic agreements with other banks, each of which then sells a portion of the IPO. Such an agreement is formed when the main investment bank want to spread the risk of an IPO across many banks.
Some of the documents that have to be drafted by the underwriters are:
- Engagement letter
- Letter of Intent
- Underwriting Agreement
- Registration Statement
- Red Herring Document
Pricing
The effective date is determined once the SEC approves the IPO. On the day before the effective date, the issuing company and the underwriter agree on the offer price (i.e., the price at which the issuing company would sell the shares) and the exact number of shares to be sold. The offer price must be determined since it is the price at which the issuing firm raises funds for itself.
Stabilization
After bringing the issue to market, the underwriter must offer analyst recommendations, after-market stabilisation, and the creation of a market for the shares issued.
In the case of order imbalances, the underwriter performs after-market stabilisation by acquiring shares at or below the offering price.
Stabilization efforts can only be carried out for a limited time; nevertheless, during this time, the underwriter has the flexibility to trade and affect the price of the issue since price manipulation rules are suspended.
Transition to Market Competition
The last step of the IPO process, the transition to market competition, begins 25 days following the initial public offering when the SEC-mandated "silent period" expires.
During this time, investors shift from relying on mandated disclosures and prospectuses to depending on market forces for information about their stocks. After the 25-day period has passed, underwriters can submit estimates for the issuing company's earnings and value. As a result, after the issue is made, the underwriter takes on the responsibilities of counsellor and assessor.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Going Public
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Capital can be used to fund research and development, capital expenditure, or pay off existing debt. | Public companies are regulated by the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 which may be difficult for newer public companies |
| Increased public awareness of the company | Must meet other rules and regulations that are monitored by the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) |
| Used by founding individuals as an exit strategy | The cost of complying with regulatory requirements can be very high. |
As previously said, the most obvious advantage is the cash reward in the form of capital raising. Capital can be utilised to support R&D, capital spending, or even to pay off current debt.
Another benefit is greater public knowledge of the firm, as IPOs frequently generate awareness by introducing their products to a new set of potential clients. As a result of this, the company's market share may rise. An IPO may also be utilised as an exit strategy by founding members. Many venture capitalists have utilised initial public offerings (IPOs) to profit from successful firms that they helped launch.
Even with the benefits of an IPO, public firms frequently encounter a number of disadvantages that may cause them to reconsider going public. One of the most significant developments is the requirement for more investor transparency.
Furthermore, public corporations are subject to quarterly financial reporting requirements under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, which may be onerous for newer public companies. They must also comply with other laws and regulations overseen by the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC).
More significantly, especially for startups, the expense of complying with regulatory standards can be prohibitively expensive. The creation of financial reporting documentation, audit fees, investor relations departments, and accounting oversight committees are all examples of added expenditures.
Conclusion
When investing in IPOs, you should seek the advice of a financial expert and proceed with caution. If you are fortunate enough to obtain an allocation of shares at the offering price of an IPO, be careful to conduct comprehensive research and due diligence before investing.
Remember that an IPO's price might go below its offering price when it hits the public market—it doesn't necessarily go higher.
References
What Is an Initial Public Offering (IPO)?
Investing In IPOs And Other Equity New Issue Offerings
IPO Process
What Are The Advantages and Disadvantages Of A Company Going Public?
Seeking funds is not a new thing for startup companies and there are various reasons why a company needs them. Their goals would play a crucial part in deciding the best way for it to generate funding.
Venture Capital (VC) and Equity Crowdfunding in Malaysia (ECF) are two of the most prevalent ways for businesses to generate funds. Traditional financing techniques, such as Venture Capital, give significant quantities of money from a small number of people, whereas ECF provides many small sums of money from a large number of people. According to the Securities Commission, Equity Crowdfunding has grown in popularity in Malaysia in recent years.
What Is Crowdfunding?
The utilisation of fair sums of funds from a large number of people to support a new business initiative is known as crowdfunding. Crowdfunding uses social media and crowdfunding platforms to connect investors and entrepreneurs, with the intention to encourage entrepreneurship by broadening the pool of investors beyond the typical circle of owners, families, and venture capitalists.
Types of Crowdfunding
There are many various forms of crowdfunding just as there are many different sorts of capital round raises for firms at all phases of development. The sort of product or service you offer, as well as your development objectives, will determine the crowdfunding approach you use. Donation-based, rewards-based, peer to peer-based and equity crowdfunding are the four main forms.
Donation-based
Donation-based crowdfunding, in general, refers to any crowdfunding effort in which the investors or donors do not receive a financial return. Disaster assistance, charities, organisations, and medical expenses are all examples of donation-based crowdfunding campaigns.
Rewards-based
Individuals who participate in rewards-based crowdfunding are expecting an exchange for a "reward," which is often a form of the product or service your firm provides. Despite the fact that this technique provides a reward to supporters, it is still considered a subset of donation-based crowdsourcing because there is no cash or equity return.
Equity Crowdfunding
Unlike donation- and rewards-based crowdfunding, equity-based crowdfunding allows contributors to become part-owners of your business by exchanging money for equity shares. Your contributions will receive a financial return on their investment as equity owners, as well as a portion of the earnings in the form of a dividend or distribution.
Peer to Peer Crowdfunding
This type of crowdfunding is often known as debt crowdfunding, which works similarly to a bank's term loan. You don't get the money from an institution; instead, you get it from individual people. This sort of crowdfunding is a little more sophisticated, involving mini-bonds, invoice financing and peer to peer lending.
Crowdfunding in Malaysia
Crowdfunding in Malaysia succeeds and grows through the supports given by the government who sees it as an opportunity to strengthen capital markets. Equity crowdfunding (ECF) providers have raised RM199 million (about $48 million) in the last five years. Despite the worldwide economic slowdown during the pandemic, the local market has grown by 278%. This is an incredible achievement for a country where alternative funding is still in its infancy. Let's look at how Malaysian equity crowdfunding got started, where it is today, and what the future holds for the industry.
The crowdfunding sector in Malaysia first started in the year 2015. The Deputy Finance Minister declared that Securities Commission (SC) Malaysia has allowed six businesses to provide crowdfunding services. Since then, 150 issuers have benefited from RM199 million collected through 159 campaigns.
In the aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic, SC Malaysia took steps to boost the investment demands on markets:
- Individuals are now eligible for a limited tax deduction for sums invested in ECF enterprises
- Limit for ECF fundraising has been increased to RM10 million.
- Companies having paid-up capital of up to RM10 million were granted access to the crowdfunding market.
- To provide exit alternatives for ECF and Peer to Peer (P2P) supporters, a secondary trading platform was developed.
As a result, issuers successfully raised RM631.04 million via ECF and P2P financing platforms in 2020 (compared to RM441.56 million in 2019). According to the regulator, 57% of funds were collected for business growth, while 97% were raised for working capital. In addition, issuers shifted to greater fundraising sums in 2020, with 84% of campaigns raising more than RM500,000.
What is Venture Capital?
Venture capital (VC) is a type of private equity and funding provided by investors to startups and small enterprises with the potential for long-term growth. Well-heeled investors, investment banks, and other financial institutions are the most common sources of venture capital. It does not necessarily have to be in the form of money; it may be in the form of technical or management skills. Small businesses with outstanding development potential, or businesses that have expanded swiftly and are set to expand, are frequently given venture capital.
Types of Venture Capital
Many forms of venture capital are categorised according to how they are used at different phases of a company's life cycle. Early-stage funding, growth financing, and acquisition/buyout financing are the three main forms of venture capital.
Early Stage Financing
Seed financing, start-up financing, and first-stage financing are the three types of early-stage financing.
Seed financing is a fair sum of money given to an entrepreneur in order for them to be eligible for a start-up loan.
Companies are provided start-up financing in order to complete the creation of goods and services. Those companies that have spent all of their initial money and require financing to launch full-scale commercial operations are the primary beneficiaries of First Stage Financing.
Expansion Financing
Second-stage finance, bridge financing, and third-stage financing are all types of expansion funding.
Second-stage finance is given to businesses to help them get started on their expansion plans. It is offered with the intention of supporting a certain firm that is expanding significantly. Companies that use Initial Public Offerings (IPOs) as the main business strategy may be eligible for bridge financing as a short-term interest-only loan or as a kind of monetary support.
Acquisition or Buyout Financing
Acquisition finance and management or leveraged buyout financing are two types of acquisition or buyout financing. Acquisition finance enables a corporation to purchase specific components or the complete company. Management or leveraged buyout finance assists management groups to acquire a specific product from another firm.
Venture Capitalist in Malaysia
Malaysia's venture capital market has always been maintained by domestic companies, and it has lagged behind industrialised nations such as Japan, Singapore, Hong Kong, Taiwan, and Korea. However, independent venture capital companies in Malaysia in the last two to three years has marked another important change in the sector.
Previously, the majority of Venture Capital Corporations (VCC) were either government or bank-owned, and all of them preferred to manage their own funds rather than outsource to professional fund management firms. In 2004, the overall amount of funds, total investments from both domestic and international sources, the number of venture capital fund management businesses, and the number of investee companies all increased.
There are 2 types of VC companies in Malaysia namely:
- Venture Capital Corporation (VCC): being a corporation that manages on its own behalf, investment in securities of venture companies in early business stages.
- Venture Capital Management Corporation (VCMC): that manages on behalf of a VCC, investment in securities of venture companies in early business stages.
Venture Capital vs Crowdfunding in Malaysia
There are some main differences between Venture Capital and Equity Crowdfunding in Malaysia. One of the main differences between them is that Venture Capital usually needs lesser effort since companies only need to convince a small number of investors to fund their business. Whereas crowdfunding usually requires more marketing momentum since companies are needed to convince a larger group of people to fund their business.
Moreover, for Venture Capital, companies need to pique the interest of the right individuals through business partner introductions or self-introductions, pitch meetings, and networking events but in crowdfunding, companies are more towards digital and online marketing such as using pay-per-click advertising, mobile marketing campaigns, e-mail informative teasers, and other digital materials to reach the largest number of investors.
| Crowdfunding | Venture Capital |
| It expands your network, allowing you to reach a broader audience and spread the word about your brand. | More advantageous for firms to aim to generate money rather than seeking to have a major social impact. However, there are chances to have contacts in key financial vehicles, which may attract the attention of other larger investors. |
| Criteria set are less strict & more flexible | Follow criteria to select investment targets & less flexible |
| More likely to get "passive investors" or "spectators, will get lesser guidance | Usually comes with a higher level of engagement, will get more guidance from investors |
| The platforms used for crowdfunding usually take 5-10% of the fundraising round on average, which is also known as "success fee" | Enable the firm to keep all of the money they received |
| The crowdfunding investor has all of the necessary information, after reading it, you can just click to invest, completely on your terms. | The valuation may not necessarily be on your terms. Venture Capitalists may request a larger stake in your business if they see the potential. |
Which One Should You Go For?
Both Equity Crowdfunding and Venture Capital funding are viable options for raising capital for your company. Make your choice depending on where you are in the lifecycle of your business and the significant differences that each of these crowdfunding techniques has to offer.
You are not limited to one single source of investment. Malaysian startups and business owners now have a lot of options because of the recent emergence of alternative business finance sources. All you need is a decent idea, a compelling pitch, and awareness of the fundings options available to you for the lifecycle of your business.
Here is some advice from the experts:
“If you have two choices, VC would be better. Because the money they are giving is very smart money. They are going to support you much more than anything. If you are running your startup alone, without VCs backing you, this means you are doing everything from scratch, but when you invite the VC on board, they have a lot of connections and a lot of experience.”
Dr Amr Hussein, CEO from Gainwells - Interviewed by Ethis
“Depending on the nature of the investor, the startup may want investors who actively help out or may want no disturbance. So, if you’re an issuer who is certain about what you are doing, go for VC, otherwise choose ECF.”
Umar Munsh, Co-Founder of Ethis
Final Thoughts
From Venture Capital to Equity Crowdfunding, there are now more diversified routes to acquire startup finance. Even though it can be challenging when it comes down to choosing whether you should focus on Venture Capital or Crowdfunding for your business, ultimately, what works best for you is determined by the nature of your firm and its objectives.
It's crucial to remember, too, that you should look into all of your financing alternatives. This may entail using crowdfunding to get your firm off the ground, followed by Venture Capital when you're ready to scale up.
References
Development of the Venture Capital Industry in Malaysia
General Overview of Venture Capital in Malaysia
How to Decide Between Crowdfunding and Venture Capitalists
Overview of Crowdfunding in Malaysia
Venture Capital vs Equity Crowdfunding: Which method is better when raising funds for your business?
10 differences between equity crowdfunding vs. traditional VC funding
Far more entrepreneurs appear to be reaching for the stars and going for the gold when it comes to raising funds for their startup enterprises via the guerilla-style bootstrapping path. What are the advantages and disadvantages of each of these approaches? What should you do if you want to succeed as a bootstrapped business?
It is easy to romanticise the idea of bootstrapping a startup. It can also work if you are motivated and willing to work hard. It may yield even greater rewards to those who can pull it off. That isn't to say that there aren't drawbacks. Make sure you understand the trade-offs and which path will bring you where you want to go.
What Is Bootstrapping?
Bootstrapping is the process of starting a business from the ground up without relying on outside funding or money. It is a method of funding small enterprises that involves the owner purchasing and employing resources at his or her own expense, rather than pooling equity or borrowing large quantities of money from banks.
Heavy reliance on domestic sources of financing, such as credit cards, mortgages, and loans is known as bootstrapping. In other words, bootstrapping is characterised by a lack of financial resources. A competent development strategy, which accounts for all conceivable hazards, is required for an enterprise's effective expansion. Furthermore, funding must be allocated to the most critical aspects of the company strategy.
Essential Stages You Have To Consider Before Bootstrapping Your Startup
Founders are frequently advised by both the startup press and social media to jump into the company blindly as soon as they have a concept. That strategy can succeed, but it's a long and difficult process that has resulted in the failure of many promising businesses. Instead, there are a few things you can do to start laying the groundwork for long-term success.
Maintain Your Day Job
The majority of bootstrappers begin with a side project while working full-time. They only leave the security of a regular job if the side hustle is a reliable, long-term source of income. This is how companies like SpaceX, Apple, Product Hunt, Trello, WeWork, Craigslist, and Twitter got their start. Never underestimate how much you can learn and accomplish in a 9-to-5 work. Getting compensated to hone your skills in a healthy, productive firm can be a fantastic foundation for whatever you're constructing.
Start It As A Side Project
Employees at Google are allowed to spend up to 20% of their time on new ideas or creative initiatives. This 20% time policy is well-known in the tech community, but it's a principle that we can all apply to our professional lives. By dabbling on the side, we can establish entire enterprises, but most significantly, side projects encourage creativity. We are free to play, explore, and learn when there's no need to hit a sales target (or make any money at all). It is a terrific method to see if the project has sparked your interest and gauge interest from others.
Share What You Create
You need to share your ideas even before they are finished, and even before they are 'ready.' One of the methods that will help you to land your first 1,000 users is to show folks what you have been working on. Bring them into your experiments, no matter how basic or unpolished they are. There are so many varied and low-cost options to share these days. Choose your preferred platform, the one that feels most natural to you and where you already spend time. A YouTube channel, an Instagram account, a podcast, or even a blog might be used.
- Before you launch a startup or try to market what you have created, build an engaged audience (even if it's small)
- Refine your thoughts. The quickest appraoch to identify unseen gaps is to explain a notion to someone else. Make the most of your pre-launch period by learning more and filling in your personal knowledge gaps.
- Create a strong track record. Business is more than just a transaction of money, it is based on trust. People get to know you better when you show them your work and take them along for the voyage. They see that you have regularly turned up, supplied useful information and completed what you started.
Continue To Learn And Stay Hungry.
It is the ideal time to study while we collect our paychecks and experiment with new ideas. Never before have we had so many professional voices and materials available to us. We can read blogs, watch videos, join meetups, listen to interviews, and read books while taking online classes. Find mentors (both real and virtual) and sponge up all the information you can. Then put what you have learned into practice and continue to experiment.
Problems, Not Emotion, Should Always Be Pursued
The finest businesses, contrary to popular belief aren't motivated by enthusiasm, they are motivated by solving issues. Ask yourself some of these questions.
- What problems have you experienced in the world?
- What problems do you have with products, services, and even yourself?
- Problems need smart solutions. Passion is just the icing on the cake.
Maintain A Deep Relationship With Your Product
Putting what you have created to good use can be a game-changer. And it appears to be straightforward, after all, who wouldn't want to use the thing they created? However, because a firm has so many moving elements, founders can easily lose sight of their original objective.
It is critical to stay close to the heart of your offering once a product or service has shipped. Use it, eat it, order it, and learn everything there is to know about it. Engagement puts you in the shoes of the consumer, allowing you to experience any issues firsthand. It also keeps the entire crew (however small) on their toes.
Advantages And Disadvantages Of Bootstrapping
Bootstrapping your startup may not be the best option for you. When weighing the benefits and drawbacks of various methods of funding, consider the advantages and disadvantages of bootstrapping to see if this self-funded path can help you achieve your objectives.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Non-dilutive financing solutions. Until you decide differently, you and your co-founders will be the only proprietors of your firm | You are investing your own money in the business. When your firm suffers a seatback, it will have a direct influence on you |
| Have more control over the route your firm takes since you don't have to keep investors satisfied allowing you to concentrate more on perfecting operations rather than worrying about mistakes. | Without cash, coaching, or introductions from someone who knows the startup ecosystem well, you will have to build your customer base and find partners on your own |
| You are forced to establish a business model that works and can generate a positive cash flow right away. | Unable to attain exponential growth. Will most likely concentrate on creating a minimum viable product or simply keeping their business afloat. |
As a solo entrepreneur, bootstrapping means keeping 100% ownership of your company. Even if you have a few co-founders, your part of the equity will be far larger than if you go through numerous rounds of funding and keep diluting your ownership. When you accept outside funding, you accept external pressure and duty to meet the needs of others. Those could be totally different from what you have in mind. Their priorities and timelines may differ from yours.
When it comes to raising funds, there are options such as super-voting rights that might give you more authority. Bootstrapping, on the other hand, is probably the way to go if artistic direction and control over decisions are high priorities for you. It is no secret that many of today's fast-growing, high-value firms, and even initial public offerings (IPOs), have been losing money.
Despite having less debt to worry about, self-funded enterprises are more likely to experience cash flow stagnation or run out of money entirely. It can be difficult to get the contacts you need to create your brand, prototypes, and more without the support of experienced investors. Bootstrapping your startup may prevent you from being able to spend thousands of dollars on Google, social media, and other marketing channels to build interest.
At the same time, if you are bootstrapping, you don't want to attract too much attention. You might not be able to keep up with high demand if you have a limited budget. The safest choice may be to keep the company's growth gradual.
Tips For A Successful Bootstrapping
It is impossible to deny that the bootstrapping process can be difficult. Because capital is sometimes a game-changer, working on a limited budget necessitates extra effort. Fortunately, you would not be the first person to bootstrap a company. There are plenty of proven strategies you may use to get the most out of your personal savings. Here are a few examples.
Recognize Cost-Cutting Opportunities
Many businesses select the lean startup method when bootstrapping. They concentrate on developing a minimum viable product using this strategy. This helps you generate income while also providing you with vital information about your customers and how to enhance your product.
Connect The Dots
When you are bootstrapping, your support network can make a big difference. Great relationships can be your strongest resources when you don't have significant investors backing you up. Begin networking to identify possible clients, collaborators, mentors, and others who can assist you in spreading the word about your company.
Don't Go Overboard
It is tempting to throw everything you've got into a project you are enthusiastic about. However, you must exercise caution. Building a business is risky enough, and bootstrapping can make it even worse. You should always have a backup plan and be willing to walk away if required during the bootstrapping process.
Having a backup plan doesn't imply you have to stay in your full-time work until your company is stable. You have the ability to dedicate yourself to achieving your goals. However, you will need to set aside some personal funds that aren't touched by your business and be aware of when you need to back out.
How To Decide If You Should Bootstrap Or Fundraise?
If you are the founder of a teach business, it won't be long before you are under pressure to raise money. You may believe that financing is the greatest approach to achieving your business goals. It may also appear to be the quickest approach to achieve your larger goals or accelerate your progress.
Those things are sometimes true but not always. Pursuing finance can come with its own set of issues, such as a loss of control, shrinking founder equity, and a draining of time and energy that could be better spent elsewhere. So here are some questions to help you decide which path you should take.
What Is Your Motivation For Seeking Funding?
Many company founders throughout the world, automatically go down the funding route because they assume it's the inevitable next step, without ever questioning why.
"Why do we need funding?" This should be your first inquiry since if you don't have a solid response, you are probably just jumping on a bandwagon that is not suited for you. In fact, bootstrapping might be preferable if you are looking for cash because that is what tech startups do. You need money since it will make your life easier and more pleasant, such as allowing you to upgrade your office space. For founders, the latter is a particularly attractive trap.
Bootstrapping forces you to ruthlessly prioritize a pool your spending and cut away unnecessary expenses, but having a pool of venture money forces you to have much more discipline when it comes to spending money.
Emerson Spaetz, Founder Of Viral Media Company, Dose
Funding, on the other hand, is more suitable for you if you have a limited window of market opportunity, and money will enable you to move quickly and completely capitalize on it. You are searching for the specialised knowledge and expertise that venture capital can provide, and you have done your homework on whose investment you want. The argument is that if you can achieve your objectives without outside finance, although at a slower pace and with less comfort, bootstrapping may be a better choice, for the time being.
What Are Your Long-Term Objectives And Plans?
Examining if your long-term goals and vision coincide with those of your investor is an important element of selecting whether to pursue finances. The prospect of money can be alluring, but if you and your investors aren't on the same page, you could be in for some major heartbreak down the road. You may, for example, feel pressured to make decisions and fulfil targets that are unrealistic or inconsistent with your business's initial mission. You might feel compelled to prioritise fast financial growth over your own business ambitions if you are aligned with investors who are all focused on it.
What if you are not even seeking a way out? If you are starting a business with the intention of keeping it long-term, you are probably better off bootstrapping. Venture Capital investors are more likely to expect you to have a big vision rather than a personal one.
Timing
You can spend time instilling positive practices and then raise funds once they have become ingrained in your company's culture. you can also confirm that you have found a product-market fit before investing money in gaining market dominance by waiting. However, there are practical reasons to raise before that point, such as a need for cash in the bank. If you don't have access to finance, either from savings or other sources, it is difficult to start a firm. You never know how long it will take to achieve product-market fit and reach profitability, so you will need a cash reserve to cover expenses along the way. If you want to be a market leader, on the other hand, you might want to raise sooner than later to avoid a competitor surpassing you with their own stack of chips. This factor is unique to your perception of the competitive landscape's danger level, new entrants, existing startup competitors, and incumbents.
On A Final Note
Bootstrapping is a great way to support a business because it retains ownership in the family and keeps debt to a minimum. While self-financing involves financial risk because you are using your own finances, you can make wise efforts to minimise the disadvantages and focus only on the rewards.
For many startup entrepreneurs, bootstrapping remains a viable choice. It has numerous advantages. However, be aware of the heightened risks as well as what you will need in place ahead of time if you change your mind and decide to bring in outside funds.
Reference
Advantage And Disadvantages Of Bootstrapping
How To Decide If You Should Bootstrap Or Fundraising?
Tips For A Successful Bootstrapping
Essential Stages You Have To Consider Before Bootstrapping Your Startup
The investment opportunities and methods are growing globally but this article will be specifically taking note of investments in Malaysia. This article will be touching base on investment opportunities in Malaysia, investment with a high return in Malaysia, exploring a few opportunities for investments in Malaysia for students and much more
Investments in Malaysia
You don’t need to be a millionaire to make money through smart investments. With the right information and mindset, you can leverage investment opportunities to increase both your wealth and your lifestyle. Taking a hypothetical situation, here is how you can invest your RM10,000 according to AIA:
-
Understand how much risk you are comfortable with. It is an individual decision to understand how much risk you are willing to take when looking for a return on your investment. It is recommended for investments in Malaysia, to establishing a safety net of up to six month’s salary before entering into investments. This enables you more room to go after those bigger risk-reward investment options that can pay off big time in the long run.
-
Fixed Deposits (FD) offer a great low-risk option. If you put your money into a fixed deposit, you can find accounts paying around 3 – 4% interest rate. You can make your money work harder for you by making this simple switch.
Also note that fixed deposit investments in Malaysia are covered for up to RM 250,000 (source: Perbadanan Insurans Deposit Malaysia), making it a low-risk investment option offering steady returns. That said, fixed deposits still operate below inflation, so if you want to grow your wealth considerably, it may not be the best option.
-
Trading shares offers reward but at great risk. The epitome of the investment portfolio, buying shares and becoming a shareholder of a listed company offers the promise of great returns. The key is to find quality companies that are undervalued in the market. This could be start-ups that are just about to take off or struggling businesses with room to bounce back stronger.
- Diversify your investment. If there is one rule to live by, it is that you should look to diversify your income streams so as not to be overly reliant upon one single stream. The same is true for your RM 10,000. Look to balance your low-level risk and riskier investments to ensure you are taking advantage of the benefits from all investment types. From the steady interest of fixed deposits to commodity trading, and investing in shares. By incorporating each into your overall investment portfolio, you will be better able to overcome any issues with a single investment item.
By exploring the investment options listed above, you will be well on your way to building your wealth. Although, as with anything wealth-related, markets and investments can fluctuate up, and down. So please, do seek consistent professional financial advice and do not solely rely upon this article for financial decisions.
Types of Investment Options in Malaysia
Options for investments in Malaysia can be assessed in many ways.
Unit Trust
A unit trust is simply a portfolio that is made up of shares, real estate, and bonds. The portfolio is then broken into units which are then sold to their customers with a profit. This is one of the options for investment in Malaysia. Maybank offers Unit Trusts, through buying units into the trust, your money will be pooled with that of other investors and invested according to the unit trust’s objectives.
The purpose is to diversify your investment portfolio, achieve economies of scale as well as be able to tap into faraway markets. Unit trusts are offered via direct banking channels or via platforms like iFast or eUnitTrust, which, ironically can be ‘cheaper’ in terms of upfront costs (aka sales charge), most of the time.
Below is a short introduction to understanding what unit trusts are.
Angel Investors
Secondly, angel investors are quite active when it comes to investments in Malaysia. NEXEA Group Sdn Bhd (Formerly known as NEXEA Angels Sdn Bhd) are valuable for startups in Malaysia because they are not as focused on monetary gains as traditional sources of funding. Instead, most angel investors have already achieved success in their careers and are now looking for ways to give back and support ideas and entrepreneurs.
The way NEXEA Group works is, that startups and businesses that require investment send us your startup funding application via this form so that we can process your application as fast as possible. Our Venture Partners will attend to your application and get back to you within a week via email. We will usually call for an initial meeting to understand more about your Startup and then meet again with Investors if you are ready for funding. We will then proceed to negotiations and draft the term sheet and make the investment.
Learn more about our Angel Investors Network and Portfolio here!
Are you an angel investor? For investment in Malaysia, if you are, you should register yourself as an Accredited Angel Investor with MBAN. You would then be eligible to enjoy a tax benefit amounting to RM 500,000 under the Angel Tax Incentive Programme. This would reduce the risk of angel investing which is high risk and high reward. You must fulfil the following criteria(s):
- Either a high net worth individual (total wealth or net personal assets of RM3million and above or it’s equivalent in foreign currencies)
- Tax resident in Malaysia
- A high-income earner (gross total annual income of not less than RM180,000 in the preceding 12 months; or RM250,000 jointly with one’s spouse)
Bonds
Amongst all the options for investments in Malaysia, bonds are also considered one of them. The main reason that investors add bonds to their portfolios is to add variety. By diversifying your investments, you reduce the risk and improve the chances of a better return on your money because bonds are relatively low risk.
Keeping a mixed portfolio that includes bonds, stocks and cash as a base of investments is a good idea; if there is a downturn in a segment of the market you do not lose all of your wealth in one go.
For bond investments in Malaysia, you can buy almost any bond at your brokerage or local bank. Brokers charge a small commission or they may mark up the bond price instead – clarify this with your broker before confirming that you want to buy.
Fixed Deposits (FD)
Think of a fixed deposit as a time capsule for your money. Once you put your money in a fixed deposit account, you can’t take it out until your agreed-upon tenure is ended. Fixed deposits offer a much higher interest rate than your average savings account - after your tenure ends
Generally, interest rates of fixed deposits in Malaysia range between 3% to 4%. Here is a table below on the updated interest rates updated as of February 2021.
| Bank | Interest Rate Offered |
| AffinBank FD | 4.05% p.a. |
| RHB Ordinary FD | 3.35% p.a |
| Alliance Bank FD | 3.35% p.a. |
| Maybank FD Account | 3.35% p.a. |
| CIMB Unfixed Deposit | 3.35% p.a. |
To start investments in Malaysia for FD's, all you need to do is sign up with the respective bank. Just remember that you’ll need to make a minimum deposit - which can be from RM1,000 up to RM5,000 - depending on which bank you opt for.
Property
Another option for investments in Malaysia is property. According to iProperty, there are a few steps involved in the due diligence process that an individual needs to go through. They are as follows:
- Decide which type of property to invest in. Whether you are to invest in a residential or commercial property. Under this residential, the 4 popular options are Terrace house, Semi-Detach House, Detach house (bungalows) and High Rise or strata residential properties such as condominiums, serviced residences and apartments.
Investments in Malaysia's commercial units such as shop lots and office lots require a much bigger downpayment as these units are usually priced over RM1 million.
- Are you planning for a short-term or a long-term investment? Long term investment, your “money” will be tied up for years. Considering you have the holding power to invest your monies for at least 5 years. Short term investment yield, you can think to buy to sell properties. In such cases, you will be cashing out your money within 2-3 years’ time, sometimes even less.
- In terms of property investments in Malaysia, do take note of the closing costs. The data below is provided by iProperty:
Legal Fee
| PRICE TIER | LEGAL FEE (% of property price) |
| First RM500,000 | 1% |
| Next 500,000 (RM500,001 – RM1 million) | 0.8% |
| Following RM2,000,000 (RM1,000,001 – RM3 million) | 0.7% |
| Next RM2,000,000 (RM3,000,001 – RM5 million) | 0.6% |
| Thereafter (> RM5 million) | 0.5% |
Stamp Duty
| Property Purchase Price | Stamp Duty |
| For the first RM100,000 | 1.00% |
| RM101,000 – RM500,000 | 2.00% |
| RM501,000 – RM1000,000 | 3.00% |
| RM1,000,000 | 4.00% |
Why Malaysia?
There are many reasons why investments in Malaysia are considered a wise decision to be made.
Having built such a strong economic foundation, Malaysia is on track to achieve its vision of becoming a high-income country.
Its remarkable economic transformation has created a myriad of opportunities for the global business community to share the benefits. With the ASEAN Economic Community coming into fulfilment and Malaysia being strategically located, now is an opportune time for the greater global business community to join Malaysia’s growth story, and capitalise on its potential as a gateway to a regional market of over 600 million people with a GDP of more than US$2 trillion.

Malaysia has also been recognised as having the most developed and sophisticated ecosystem for the Islamic economy out of the 70 countries surveyed in Thomson Reuters’ The State of Global Islamic Economy 2014/2015 Report. It tops four of the six sub-sectors including the higher weighted Islamic finance, halal food, halal tourism, and pharmaceuticals and cosmetics sectors.
To increase the number of investors in the country, the government has come up with some favourable policies. These include:
- Access to government-sponsored industrial estates.
- Grants and loans from government agencies.
- A wide range of tax deductions.
Among the Asian emerging markets, investments in Malaysia have proved to be unique regarding comparative advantages.
Investments In Malaysia for Young Professionals
With the average starting salary for fresh graduates in Malaysia ranging from RM2,300 to RM2,500 combined with the rising cost of living, it comes as no surprise that there is a huge percentage of Gen-Y who are now stuck in a rat race. Research studies by Malaysian Digest have shown that millennials are earning less when compared to their parents at the same age. This leads them to think of putting in investments in Malaysia starting as early as they can.
To promote young professionals for investments in Malaysia, firms should not just tell them how investment reaps money but instead show them how compounding can help them turn time into money. To encourage professionals, an example used by Forbes is illustrated below:
It assumes a constant 8% return for two investors: one who starts early in life and one who starts 11 years later.
Investor #1 (blue line) starts investing $2,000 a year at age 19 through 27. Then she stops adding money to her account and just stays invested until age 65. Investor #2 (orange line), on the other hand, waits until she’s 30 years old to start investing. She diligently invests $2,000 a year for the next 36 years. By age 65, she’s contributed a total of $72,000 to her investments, and yet she ends up with less money than Investor #1 simply because she missed the opportunity to compound gains on 11 years of growth and contributions.
However, do take note that this is a hypothetical example only and investments in Malaysia may not always churn out the same result.
List of Investment Companies in Malaysia
An investment company is a business, which as the name suggest their core activity is investing and identifying investment opportunities. This term is quite broad. An investment company can invest in anything from real estate to stocks. But what are the requirements to be called an investment company?
An Investment company should always be operating with a fund of capital supplied by investors, making it a pooled fund of capital. Investment companies could be either publicly (traded on the stock market) or privately owned. Some investment companies are listed, most are not. There are three (3) types of investment companies: closed-end funds, mutual funds and Unit Investment Trusts
See our insight into the list of investment companies in Malaysia 2020
Other than angel investors, there are a lot of opportunities that investors can use to make investments in Malaysia. This includes other methods like venture capital, hedge funds and equity crowdfunding.
Venture capital – These forms of investments in Malaysia involves an investor who supplies money and guidance to a growing company in exchange for the equity of the company.
Hedge funds – This is a pooled fund of capital managed by an investment expert, very similar to the three types of investment companies mentioned previously. Hedge funds, however, have a larger barrier to entry. The capital in hedge funds provided by one investor is usually a lot more than in an investment company.
Do’s and Don’ts of Investing
There are pros and cons to all processes, investments in Malaysia particularly are no different. Investments in Malaysia come with their own set of dos and don'ts. However, do note that these restrictions and concerns are not only limited to investments in Malaysia but generally as well.
- Do assess and educate yourself. Choose a financial advisor to guide you in the process, and also make sure he or she has adequate experience and knowledge about investing.
- Do diversify. A diversified portfolio should not only be varied in its number of investments but also in types of investments. In the event that one or two of your stocks begin performing poorly, it may not affect your entire portfolio greatly. This is just one reason why your stock portfolio should be sufficiently diversified.
- Don't speculate or over-estimate. You are likely to get unsolicited advice from stock trading sources. However, you should never invest blindly in free tips or recommendations, even if they do sound appealing. Trust your advisor to guide you in the right direction when it comes to investing decisions.
- While investing, you should never take unnecessary risks, as your risk-reward should always be balanced. A good advisor will tell you that it’s never a good move to invest all your money in hot stock to get a slightly higher return. On the contrary, safeguarding your money is just as important as getting high returns.
To Conclude
Investments in Malaysia offers a lot of options, from angel investments to FD's to investing in property. The ideal way to decide is to create your own checklist along with a financial advisor from a professional consultant.
Your checklist should include, your preferred period for the investment, the amount, risk you are willing to take, the amount of money you are willing to input along with an advisory from your consultant on the better choice of investment for you.
References
HOW TO INVEST RM 10,000 (THE SMART WAY)
Investments in Malaysia: Maybank Unit Trusts
Investing in startups is trending, but the million-dollar question is why people tend to invest in startups, how to generate outsized returns through investing your money in a startup, are there any companies that specialise in funding and investing startups and the list doesn’t end there.
Mature organisations of course have innovation agendas – whether they involve significant research and development budgets or corporate innovation frameworks – but often the core DNA of these cultures are missing. This is where startups step into the game.
Why Invest in Startups?
Investors and people choose to invest their money so at a later stage it either multiplies or grows in value. Many investors and people also tend to invest in startups rather than fully operational running companies. Before taking an investment decision, many investors and people tend to find statistics regarding the industry the startup is based in, or generally the success rate of previous records that have taken the leap to invest in startups.
Forbes identifies four reasons why people tend to invest in startups:
- Potentially generating uncorrelated outsized returns and provides portfolio diversification.
- Diversify. Investing in unique and creative startups will not only create a unique selling point in the product and service you are selling but also be able to diversify an investors portfolio. Diversification in investment will not only spread out the risk of loss but also create a wider scope of profit.
- Networking. Startups are hyper-innovators driven by crazy ambition and insight. Being an early-stage investor in a startup is ideal for networking because you are closely linked to founders team and the company structure itself.
- Craving to be involved in driving positive change, bringing new solutions to life. This is to be able to support the entrepreneurs’ vision solely, empowering and boosting the confidence of the entrepreneurs as well as supporting small businesses.
Analyze The Startup
Before you actually dive deep to invest in startups, there is a criterion and a particular checklist that you need to go through in order to secure the investment decision.
How To Find The Right Startups To Invest In: A Checklist
So, you’re ready to add to your investment portfolio. Now you’re looking to learn how to find startups to invest in. Here’s what you need to know to find your next investment.
-
Determine what kind of an investor you are. The two main types of investors that invest in startups; angel investors and venture capitalists. An angel investor usually has a high net worth and provides financial backing for small startups or entrepreneurs. A venture capitalist (VC) makes an investment that provides financial backing to firms with high growth potential in exchange for an equity stake.
If you prefer to work alone and at the start of a company, being an angel investor might be better for you, while those who work well with others should veer toward being a venture capitalist, as they work with a company. Alexis Ohanian, an entrepreneur and investor in Brooklyn, NY, best known as the co-founder and executive chair of Reddit, focuses on seed investments.
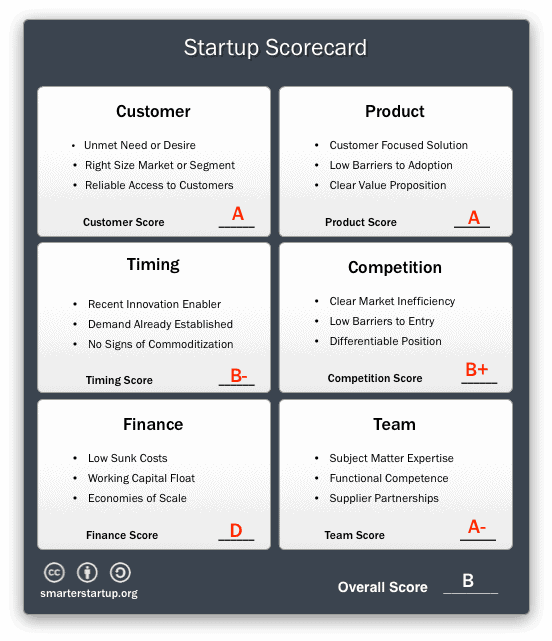
-
Perform investment analysis. Before making the decision to invest in startups, ask yourself the following qualitative questions: Is the founder financially invested in some way? Is there healthy chemistry and communication between the entrepreneur and yourself (the investor)? Does it have a sustainable competitive edge/advantage – in regard to the business model, brand, distribution, operations, patent ownership/intellectual property, unique ability to innovate, etc.? Does it solve a major problem or pain point in a big way?
The quantitative research shall include: consulting the numbers, key company statistics, and financial documents. They help disclose a business’s performance, competitive positioning, and potential risks. -
What are you looking for in a startup investment pitch? As an investor, before you invest in startups, it is important to scan through their investment pitch and see what the business is all about. This is a moment of truth for the startup, as you should be looking for several things throughout a pitch that will determine a “yes” or “no” to this investment. Ideally, the startup founder will be highly knowledgeable in the product’s field, will know the company’s toughest competitors, and be well-informed of the current industry climate and trends and this should reflect in an entrepreneurs pitch.
As an investor, you should look for whether the business has set realistic expectations for their current and future projections. Entrepreneurs should give you, the potential investor, exact amounts for their desired investments. They should also project the use of these funds in scaling the business. Additionally, they should review what they expect their ROI to be.
When determining how to find a startup to invest in, most investors will go straight to the product. A product prototype is crucial to your understanding of what customers will see and experience.
Visit our guide to The Pitch Deck Guide: The 12 Top Slides you Need to get tips and guidance in order to create the perfect investment pitch.
Investment Approach To Startups
Startups are hyper-innovators driven by crazy ambition and insight. What makes startup investing interesting compared to other investment classes is that often startups can’t (and shouldn’t) be able to provide the level of forecasting or comparable market data as other investment propositions.
These characteristics of startups affect the way that they are valued and types of data that investors look for before they invest in startups. Investing in startups, by default, requires a different approach, to which Bill Gross’s ‘Ted Talk’ provides a great foundational overview. Here are a few things that are important to consider:
- Gain a deep understanding, not only of the problem that the startup is solving but the driving factors to why that problem exists and why now is the time for a solution
- Don’t get fixated on financial forecasts. Understand the drivers to the startup’s growth – and its customer acquisition
- Invest alongside others – group investment and co-investment is a growing space for a reason
For most investors, startups comprise a small part of their overall portfolio for good reason. This is important for startups to note as well: You can’t over communicate with your investors. Engage them in the right way, and they will be there through thick and thin.
How Much Should You Invest in Startups?
How much should one invest in startups? According to the U.S. Small Business Administration, most startups cost around $3,000 to begin, while most home-based franchises cost $2,000 to $5,000. It’s important to understand the different types of costs you’ll have as a new business.
Theoretically, it’s good to take note of what costs are fixed, variable, essential or optional. But let’s get concrete. Here’s a shortlist of costs you’ll likely have as a new business:
- Web hosting and other website costs
- Rental space for an office
- Office furniture
- Labour
- Basic supplies
- Basic technology
- Insurance, license or permit fees
- Advertising or promotions
- Business plan costs
According to Business News Daily, below is an estimate of how much it costs to run a startup initially. This estimate should help you plan out your finances and understand the opportunities you have on hand to explain to investors who are keen to invest in startups.
| Item | Details | Estimated cost |
| Rent | Office space membership | $2,750 |
| Website | Design and hosting | $2,000 |
| Payroll | 5 employees with a $35K/year salary | $175,000 |
| Advertising/promotion | Digital ads cost | $5,000 |
| Basic office supplies | Paper, pens, etc. | $80 |
| Total (annualized) | -- | $184,830 |
Are Startups A Good Investment?: An Investor’s Take
Entrepreneur-turned-angel investor Sanjay Mehta has been one of the most active angel investors in India, having participated in early rounds for over 137 startups in his personal capacity. Mehta also recently invested in 20 early-stage startups — out of a planned 100 — in December 2019, through his new venture fund 100X.VC. He is founder & partner at 100X.Venture Capital in Mumbai.
“One basic fundamental that every early-stage investor should know is that startups follow the law of power – a small per cent of the startups you invest in will give you the majority of your profits”.
Sanjay Mehta, founder & partner at 100X.Venture
“Are startups a good investment?” Startups are high risk and high return investments, which follow the power of law. It is not about the number of hits you have, but the magnitude of those hits. That’s where we find the answer to our question. The wealth creation opportunity that startup investments provide is nearly unparalleled. But it is also extremely risky, and conditional.
According to Sanjay Mehta’s experience, you must be willing to invest in startups when one has the appetite and the capacity for the high risk involved. An investor with a mission to give first, help founders, and build a business will win this game. One must be capable of creating a significantly sized portfolio of investments in the hope that some of the investments are part of the six per cent and give one huge return.
One can create a startup portfolio by investing about five to ten per cent of their total investment capacity in such an illiquid asset class. It is worth noting that the money invested here must be thought of as a sunk cost – until and unless an exit is realised. The investors must be able to stay patient with their capital that they invest in startups – the best companies can give returns only after 10 years.
It is a great idea to invest in startups if you have access to the funds, the patience to wait for returns and commitment to nurturing the entrepreneur and the business itself. But an individual can invest in startups that can give unparalleled returns you hope for if they work out. To gain access to the top startups, one has to put in time and effort to become a part of the startup ecosystem, become a part of various investor networks, and collaborating with other lead investors and VC firms.
Companies That Invest in Startups
A tech startup is a company whose purpose is to bring technology products or services to market. These companies deliver new technology products or services or deliver existing technology products or services in new ways.
What Is A Tech Startup?
A tech startup is a company created to develop new technology-based products/services or to deliver existing tech-based products/services in new and interesting ways.
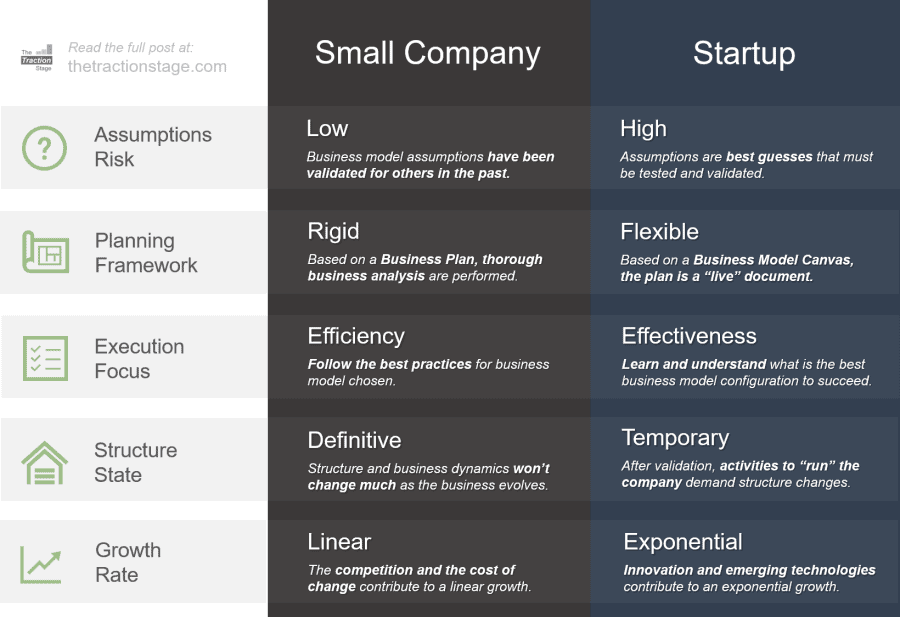
In order for a startup to become successful, it must establish itself as a leader within a particular industry, often referred to as “establishing market-share”, or “achieving market domination.” In more precision, a tech startup can be an organization formed to search for a repeatable and scalable business model, that is potentially producing and selling technological products – whether those are software, hardware or both. This does not make the process to invest in startups any different.
A newly founded startup must carefully select its target market and demographic to ensure it has a fair shot at establishing market-share. Often, founders will evaluate startup ideas based on the opportunities available within a given market.
NEXEA’s Angel Investor Network is ideal for startups in Malaysia. Our Angel Investors Network provides startup investment opportunities to investors that are interested in high growth businesses. These are high risk & high return investment opportunities that should be part of any investor’s portfolio as this is the segment of the portfolio that produces good ROI.
Testimonials by NEXEA Funded Startups
NEXEA’s expertise is startup funding and knows and understands how to invest in startups. The testimonials by NEXEA funded startups like RunningMan, JomRun and Red Dino contribute to our list of successfully funded startups.
Click here to learn more about the benefits that startups reap through NEXEA funding. Also, view our Portfolio.
Invest In Tech Startups: GGV To Invest Further RM75m Into Malaysia Tech Startups
Golden Gate Ventures, a Singapore venture capital firm, announced the opening its Malaysian office in Kuala Lumpur in late 2018. Having already utilised a quarter of its Fund II in early-stage tech companies that are based in or operating in Malaysia, the firm now plans to invest another MYR75 million (US$18 million) to help back Malaysian based start-ups.
According to the company, Malaysia – as the second-most developed economy in ASEAN – noted that the country has strong fundamentals in place to sustainably grow its already-vigorous start-up scene, as it possesses the region’s highest rate of initial public offerings (IPOs) as well as high digital penetration.
From Golden Gate Ventures Partner Justin Hall, this, alongside the nation’s consistently growing economy, makes it a microcosm of the greater Southeast Asian economy.
“Malaysia is a natural market to expand to for startups. The domestic ecosystem itself is so large and diverse that businesses find an increasingly deep opportunity and a welcome market for their products and services” said Tee. “For Homage, we are looking at Malaysia to help support the local aged and meet their fast-growing care needs. We see the signs and opportunities for aged care solutions to grow sustainably with collaborative support from stakeholders across the private and public sector.”
Gillian Tee, the CEO of Homage, explained that Golden Gate Ventures expansion into Malaysia has also coincided with her firm’s own entry into the market
Malaysia is the third and latest location in Southeast Asia for Golden Gate Ventures, after Singapore and Indonesia. To date, the firm already has several innovative start-ups operating in Malaysia in its portfolio.
Malaysian Government Incentives During COVID-19
These incentives for tech startups come as a boost for Malaysian startups at the time of the new normal, says Finance Minister Tengku Datuk Seri Zafrul. It was introduced as part of the government’s economic stimulus package to weather the impact of the Covid-19 pandemic on startups. It had attracted eight VC fund managers from the United States, South Korea, China, Indonesia and Singapore to invest in Malaysian startups as part of the RM1.2bil programme to help facilitate a growth path and a vibrant ecosystem for high-potential firms to thrive in.
On A Final Note
How you search and invest in startups is an important part of success. You don’t want to spend years crisscrossing the country in search of investment opportunities without making any actual investments. Wherever possible you want to optimize the process and costs so that you make the process to invest in startups efficiently. How to invest in startups is only the initial stage however, what comes after is solely the responsibility and the autonomy lies within the entrepreneur.
References
GGV To Invest Further RM75m Into Malaysia Tech Startups
How To Invest In Startups And Make Money
https://thetractionstage.com/2018/10/08/a-startup-or-a-small-company-that-is-the-question/
This article will supply you with a list of investment companies in Malaysia. To understand the value of this list to a potential investor, a brief description of an investment company is mentioned as well as the different types of investment companies. Lastly, the main steps of investing are given and different opportunities to invest in.
What is an investment company?
An investment company is a business, which as the name suggest their core activity is investing and identifying investment opportunities. This term is quite broad. An investment company can invest in anything from real estate to stocks. But what are the requirements to be called an investment company?
An Investment company should always be operating with a fund of capital supplied by investors, making it a pooled fund of capital. Investment companies could be either publicly (traded on the stock market) or privately owned. Some investment companies are listed, most are not.
In most cases when mentioning an investment company. It is a company that makes a profit by buying and selling shares.
Three types of investment companies
The three types of investment companies are closed-end funds, mutual funds (open-end funds), and unit investments trusts. They all have different qualities which will be explained in this section of the article.
Closed-end funds
These investment companies are traded on the stock exchange. As it is a closed-end fund, there is a fixed number of shares outstanding. Which results in that trading these stocks do not have any influence on their portfolio.
Mutual fund
These companies have a floating number of shares. So, the fund can become larger and smaller, this depends on the amount of total capital invested. When there are more shares outstanding there is more capital put into the fund, therefore the fund is larger. This structure can be more complex for investment managers as they have to plan for the possibilities that investors want to get all their money back at a sudden.
Unit investment trusts
These investment companies are very similar to the mutual fund type. As these are like the mutual fund redeemable investment (shares). The main difference between the two is their legal structure. A mutual fund is a company, while unit investment trusts are not.
List of investment companies in Malaysia
Unit trust companies
AmChina A – Shares
Kenanga Growth Opportunities Fund
TA Global Technology Fund
Principal Global Tech Fund-MYR Hedged
Closed-end funds
TA Investment Management (Islamic fund)

Steps to selecting an investment company
What are your goals?
It is important to know your goals in order to select the correct investment firm for you. Some may like a more defensive approach. Investors hope this will result in a lower return but a more stable return. Some investors pick the aggressive approach which consists of very risky investments, aiming for a high return in a small amount of time.
When do you require a return?
Some investors, invest to get a rerun in the long-run. This could be beneficial as returns are usually higher and more stable. However, most investors do not have a large sum of money available over a long period. Some unfortunate things may happen, for example, an unforeseen renovation or a broken car. That is why it is so important to predict your expenditures, and know when you require to have a return back on your investment.
Make an investment plan
This plan should consist of the previously discussed aspects, the risk you are willing to take and when you want a return. Furthermore, you should think about what industry you would like to invest in. When selecting an investment company find out in what industries they invest in, and whether or not this is suitable for you. The industry you want to invest in depends on your preference. Some are interested in green investments. While others focus on something completely different, like the automotive industry.
Diversify
In the case of an investment company, they make the choices for you. These investment companies have a very broad portfolio, so your investment should already be very diversified. However, do always consider investing in several investment companies as something unforeseen could always happen. For example, a scandal of the investment company.
How hands-on do you want to be?
This is not very applicable in an investment company as your investment is being handled by an investment expert. They will invest for you. However, if you would like to be more hands-on consider joining a venture capital or a hedge fund.
What are the charges?
Do they charge you management fees? This would not be the case with a listed company as you buy shares of them directly from the stock market. But unit trust companies could charge you fees. Ask yourself the question of what percentage you are willing to pay.
Other opportunities for investors
There are a lot of different ways to invest and a lot of different opportunities. For the purpose of this article, we want to provide you with four different methods of investing. These are venture capital, hedge funds, equity crowdfunding and lastly joining an angel investor network.
Venture capital – This type of investment involves an investor which supplies money and guidance to a growing company in exchange for equity of the company.
Hedge fund – This is a pooled fund of capital managed by an investment expert, very similar to the three types of investment companies in this article. Hedge funds, however, have a larger barrier to entry. The capital in hedge funds provided by one investor is usually a lot more than in an investment company.
Equity crowdfunding – This is a method for start-ups and growing companies to get capital in exchange for equity. The difference with VC is that there are a lot of investors involved who normally do not provide guidance.
Joining an angel investor network – Is very similar to VC however the guidance provided is far more intensive when being an angel investor. Also, the amount of capital is usually lower than the amount a VC will invest.